The Variation of Transcriptomic Perturbations is Associated with the Development and Progression of Various Diseases
- PMID: 36204511
- PMCID: PMC9530920
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2148627
The Variation of Transcriptomic Perturbations is Associated with the Development and Progression of Various Diseases
Abstract
Background: Although transcriptomic data have been widely applied to explore various diseases, few studies have investigated the association between transcriptomic perturbations and disease development in a wide variety of diseases.
Methods: Based on a previously developed algorithm for quantifying intratumor heterogeneity at the transcriptomic level, we defined the variation of transcriptomic perturbations (VTP) of a disease relative to the health status. Based on publicly available transcriptome datasets, we compared VTP values between the disease and health status and analyzed correlations between VTP values and disease progression or severity in various diseases, including neurological disorders, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, digestive diseases, and endocrine diseases. We also identified the genes and pathways whose expression perturbations correlated positively with VTP across diverse diseases.
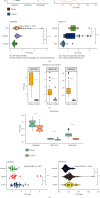
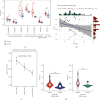
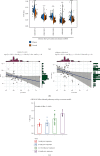
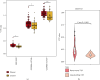
Results: VTP values were upregulated in various diseases relative to their normal controls. VTP values were significantly greater in define than in possible or probable Alzheimer's disease. VTP values were significantly larger in intensive care unit (ICU) COVID-19 patients than in non-ICU patients, and in COVID-19 patients requiring mechanical ventilatory support (MVS) than in those not requiring MVS. VTP correlated positively with viral loads in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients. Moreover, the AIDS patients treated with abacavir or zidovudine had lower VTP values than those without such therapies. In pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) patients, VTP values followed the pattern: active TB > latent TB > normal controls. VTP values were greater in clinically apparent than in presymptomatic malaria. VTP correlated negatively with the cardiac index of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), VTP showed a negative correlation with forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1). VTP values increased with H. pylori infection and were upregulated in atrophic gastritis caused by H. pylori infection. The genes and pathways whose expression perturbations correlated positively with VTP scores across diseases were mainly involved in the regulation of immune, metabolic, and cellular activities.
Conclusions: VTP is upregulated in the disease versus health status, and its upregulation is associated with disease progression and severity in various diseases. Thus, VTP has potential clinical implications for disease diagnosis and prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Zehua Dong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B . 1995;57(1):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x. - DOI
-
- Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V. K., et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 2005;102(43):15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

