Mitophagy: A Potential Target for Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Remodelling
- PMID: 36204518
- PMCID: PMC9532135
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2849985
Mitophagy: A Potential Target for Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Remodelling
Abstract
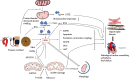
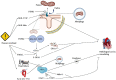
The pathological mechanisms underlying cardiac remodelling and cardiac dysfunction caused by pressure overload are poorly understood. Mitochondrial damage and functional dysfunction, including mitochondrial bioenergetic disorder, oxidative stress, and mtDNA damage, contribute to heart injury caused by pressure overload. Mitophagy, an important regulator of mitochondrial homeostasis and function, is triggered by mitochondrial damage and participates in the pathological process of cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies indicate that mitophagy plays a critical role in the pressure overload model, but evidence on the causal relationship between mitophagy abnormality and pressure overload-induced heart injury is inconclusive. This review summarises the mechanism, role, and regulation of mitophagy in the pressure overload model. It also pays special attention to active compounds that may regulate mitophagy in pressure overload, which provide clues for possible clinical applications.
Copyright © 2022 Ruochen Shao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial DNA Mutation, Diseases, and Nutrient-Regulated Mitophagy.Annu Rev Nutr. 2019 Aug 21;39:201-226. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-082018-124643. Annu Rev Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31433742 Review.
-
Oxidative Insults and Mitochondrial DNA Mutation Promote Enhanced Autophagy and Mitophagy Compromising Cell Viability in Pluripotent Cell Model of Mitochondrial Disease.Cells. 2019 Jan 17;8(1):65. doi: 10.3390/cells8010065. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30658448 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Reversible Changes Determine Diastolic Function Adaptations During Myocardial (Reverse) Remodeling.Circ Heart Fail. 2020 Nov;13(11):e006170. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006170. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Circ Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 33176457
-
Mitophagy in cardiovascular homeostasis.Mech Ageing Dev. 2020 Jun;188:111245. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111245. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020. PMID: 32289324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitophagy deficiency activates stimulator of interferon genes activation and aggravates pathogenetic cardiac remodeling.Genes Dis. 2023 Sep 2;11(6):101074. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.08.003. eCollection 2024 Nov. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 39281830 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HINT2 protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac remodelling through mitochondrial pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(8):e18276. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18276. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38546629 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Congenital Heart Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jan 25;12(2):42. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12020042. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 39997476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk among mitophagy, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and necroptosis in central nervous system injuries.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):1660-1670. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.389361. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38103229 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity with human primary cardiomyocytes.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Feb;67(2):301-319. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2369-3. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 37864082
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

