Dexmedetomidine exerts an anti-inflammatory effect via α2 adrenoceptors to alleviate cognitive dysfunction in 5xFAD mice
- PMID: 36204551
- PMCID: PMC9531904
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.978768
Dexmedetomidine exerts an anti-inflammatory effect via α2 adrenoceptors to alleviate cognitive dysfunction in 5xFAD mice
Abstract
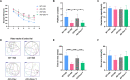
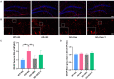
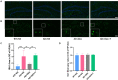
Background: Inflammation promotes the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we explored the effect of dexmedetomidine on inflammation and cognitive function in a mouse model of AD. Methods: 5xFAD mice were intragastrically administered saline, dexmedetomidine, or dexmedetomidine and yohimbine for 14 days. The effects of dexmedetomidine on the acquisition and retention of memory in the Morris water-maze test and Y maze were evaluated. The deposition of amyloid beta protein (Abeta) and cytokine levels in the hippocampus were assessed. The expression of Bace1 protein and NFκB-p65 protein was assessed by Western blotting. Results: Compared with WT mice, 5xFAD mice exhibited cognitive impairment in the Morris water maze test and Y maze test. Cognitive decline was alleviated by dexmedetomidine and this was reversed by the α2 adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine. Compared with saline treatment, dexmedetomidine led to a reduction in the Abeta deposition area (p < 0.05) and in the mean gray value (p < 0.01) in the hippocampus of 5xFAD mice. Compared with saline treatment, dexmedetomidine inhibited the activation of astrocytes and microglia in the hippocampal DG of 5xFAD mice and reduced the area of GFAP (p < 0.01) and IBA1 (p < 0.01). The level of IL-1β in the hippocampus decreased significantly after dexmedetomidine treatment compared with saline treatment in 5xFAD mice (p < 0.01). Yohimbine neutralized the effects of dexmedetomidine. Dexmedetomidine inhibited the expression of BACE1 and NF-κB p65 (p < 0.01), and these changes were reversed by yohimbine treatment. Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine alleviates cognitive decline, inhibits neuroinflammation, and prevents the deposition of Abeta in 5xFAD mice. The effect is mediated by the α2 adrenoceptor-mediated anti-inflammatory pathway. Dexmedetomidine may be effective for the treatment of AD and a better choice for the sedation of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid plaques; dexmedetomidine; neuroinflammation; yohimbine.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Li, Guo, Wang, Wang, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

