Association of Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Platelet Ratio and Mortality in Patients with Sepsis
- PMID: 36204660
- PMCID: PMC9532144
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4915887
Association of Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Platelet Ratio and Mortality in Patients with Sepsis
Abstract
Background: As a novel inflammatory index, the ratio of red cell distribution width (RDW) to platelet count (RPR) may have prognostic value in some critical illnesses. However, studies on the prognostic influence of RPR in patients with sepsis are few. This study is aimed at investigating the association between RPR levels and 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis.
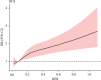
Methods: Data of patients with sepsis were obtained from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III database. The best cut-off value was calculated by establishing the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), and the predictive ability of different indicators was compared through the area under the curve (AUC). The association between RPR levels and 28-day mortality was assessed using the Cox proportional hazards model. Restrictive cubic spline analysis was applied to the multivariable Cox model to investigate the nonlinear relationship between RPR and 28-day mortality.
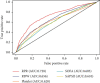
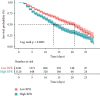
Results: A total of 3367 patients with sepsis were included in the study. A nonlinear relationship was observed between RPR and 28-day mortality, showing a trend of a first rapid increase and a gradual increase. For the prediction of mortality, the best cut-off value for RPR was 0.109, with an AUC of 0.728 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.709-0.747). The predictive capability of RPR was superior to those of RDW, platelet, SOFA score, and SAPS II score. After adjusting for various confounding factors, high RPR was significantly associated with increased mortality with adjusted hazard ratios of 1.210 (95% CI: 1.045-1.400) for categorical variables and 2.826 (95% CI: 2.025-3.944) for continuous variables.
Conclusion: Elevated RPR level is significantly correlated with a high risk of 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis and can be a new predictor of patient prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Jie Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Red Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Ratio Is Associated with Increasing In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury.Dis Markers. 2022 Jan 17;2022:4802702. doi: 10.1155/2022/4802702. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35082929 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of red blood cell distribution width, platelet distribution width, and red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio in children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Sep;35(9):e23909. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23909. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34273201 Free PMC article.
-
[Value of red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet count ratio in predicting the prognosis of children with sepsis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Nov;21(11):1079-1083. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.11.005. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31753088 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Association of red blood cell distribution width-platelet ratio with mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting.PeerJ. 2025 May 22;13:e19472. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19472. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40416608 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio for predicting staging liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e15096. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015096. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946368 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of thiamine administration and prognosis in critically ill patients with heart failure.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1162797. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1162797. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033650 Free PMC article.
-
Red cell distribution width/platelet ratio predicts decompensation of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-related compensated advanced chronic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 21;31(3):100393. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i3.100393. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39839903 Free PMC article.
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-to-Platelet Ratio Predicts 30-Day Mortality in Postoperative Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296251346174. doi: 10.1177/10760296251346174. Epub 2025 May 26. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025. PMID: 40420572 Free PMC article.
-
Combined glycated hemoglobin index and red cell distribution width predict in-hospital mortality in critically ill sepsis patients based on MIMIC-IV analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 10;15(1):12266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94179-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40210921 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of systolic blood pressure and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Aug;55(8):2099-2109. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03510-7. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36840802
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

