Maturation-based Corrective Adjustment Procedures (Mat-CAPs) in youth swimming: Evidence for restricted age-group application in females
- PMID: 36206228
- PMCID: PMC9543692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275797
Maturation-based Corrective Adjustment Procedures (Mat-CAPs) in youth swimming: Evidence for restricted age-group application in females
Abstract
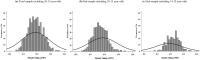
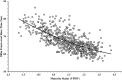
Inter-individual differences in maturation-associated development can lead to variations in physical performance, resulting in performance (dis)advantages and maturation selection bias within youth sport systems. To address such bias and account for maturational differences, Maturation-based Corrective Adjustment Procedures (Mat-CAPs) could be beneficial. The present study aimed to: (1) determine maturity timing distributions in youth female swimming; (2) quantify the relationship between maturation status and 100-m front-crawl (FC) performance; (3) implement Mat-CAPs to remove maturational influences upon swimming performance. For Aim 1 and 2, participants were 663 female (10-15 years) swimmers who participated in 100-m FC events at Australian regional, state, and national-level competitions between 2016-2020 and underwent anthropometric assessment (mass, height and sitting height) to estimate maturity timing and offset. For Aim 3, participants aged 10-13 years were categorised into maturity timing categories. Maturity timing distributions for Raw ('All', 'Top 50%' and 'Top 25%') and Correctively Adjusted swim times were examined. Chi-square, Cramer's V and Odds Ratios determined the presence of maturation biases, while Mat-CAPs identified whether such biases were removed in targeted age and selection-groups. Results identified that between 10-13 years, a significantly higher frequency of 'early' maturers was apparent, although tapered toward higher frequencies of 'Late-normative' maturers by 14-15 years. A curvilinear relationship between maturity-offset and swim performance was identified (R2 = 0.51, p<0.001) and utilised for Mat-CAPs. Following Mat-CAPs application, maturity timing biases evident in affected age-groups (10-13 years), and which were magnified at higher selection levels ('Top 50%' & '25%' of swim performances) were predominantly removed. Findings highlight how maturation advantages in females occurred until approximately 13 years old, warranting restricted Mat-CAPs application. Mat-CAPS has the potential to improve female swimmer participation experiences and evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Winand M, Zintz T, Bayle E, Robinson L. Organizational performance of Olympic sport governing bodies: dealing with measurement and priorities. Managing Leisure. 2010;15(4):279–307.
-
- Baker J, Cobley S, Schorer J, Wattie N. Talent identification and development in sport. Routledge handbook of talent identification and development in sport 2017. p. 1–8.
-
- Morais JE, Saavedra JM, Costa MJ, Silva AJ, Marinho DA, Barbosa TM. Tracking young talented swimmers: follow-up of performance and its biomechanical determinant factors. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2013;15(3). - PubMed
-
- Morais JE, Silva A, Marinho DA, Seifert L, Barbosa TM. Cluster stability as a new method to assess changes in performance and its determinant factors over a season in young swimmers. Int J Spot Physiol Perform. 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

