Understanding islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes through multidimensional pancreatic phenotyping: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program
- PMID: 36206763
- PMCID: PMC9742126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.013
Understanding islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes through multidimensional pancreatic phenotyping: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program
Abstract
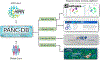
In this perspective, we provide an overview of a recently established National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) initiative, the Human Pancreas Analysis Program for Type 2 Diabetes (HPAP-T2D). This program is designed to define the molecular pathogenesis of islet dysfunction by studying human pancreatic tissue samples from organ donors with T2D. HPAP-T2D generates detailed datasets of physiological, histological, transcriptomic, epigenomic, and genomic information. Importantly, all data collected, generated, and analyzed by HPAP-T2D are made immediately and freely available through a centralized database, PANC-DB, thus providing a comprehensive data resource for the diabetes research community.
Keywords: T2D; epigenomics; islets; pancreas; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Brissova M, Fowler MJ, Nicholson WE, Chu A, Hirshberg B, Harlan DM, and Powers AC. (2005). Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 53, 1087–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous