Beyond rRNA: nucleolar transcription generates a complex network of RNAs with multiple roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis
- PMID: 36207140
- PMCID: PMC9575697
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.349969.122
Beyond rRNA: nucleolar transcription generates a complex network of RNAs with multiple roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis
Abstract
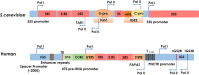
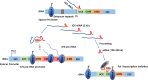
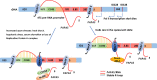
Nucleoli are the major cellular compartments for the synthesis of rRNA and assembly of ribosomes, the macromolecular complexes responsible for protein synthesis. Given the abundance of ribosomes, there is a huge demand for rRNA, which indeed constitutes ∼80% of the mass of RNA in the cell. Thus, nucleoli are characterized by extensive transcription of multiple rDNA loci by the dedicated polymerase, RNA polymerase (Pol) I. However, in addition to producing rRNAs, there is considerable additional transcription in nucleoli by RNA Pol II as well as Pol I, producing multiple noncoding (nc) and, in one instance, coding RNAs. In this review, we discuss important features of these transcripts, which often appear species-specific and reflect transcription antisense to pre-rRNA by Pol II and within the intergenic spacer regions on both strands by both Pol I and Pol II. We discuss how expression of these RNAs is regulated, their propensity to form cotranscriptional R loops, and how they modulate rRNA transcription, nucleolar structure, and cellular homeostasis more generally.
Keywords: RNA pol I; RNA pol II; ncRNAs; nucleolus.
© 2022 Feng and Manley; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleolar Pol II interactome reveals TBPL1, PAF1, and Pol I at intergenic rDNA drive rRNA biogenesis.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):9603. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54002-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39505901 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar RNA polymerase II drives ribosome biogenesis.Nature. 2020 Sep;585(7824):298-302. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2497-0. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32669707 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleolus—guardian of cellular homeostasis and genome integrity.Chromosoma. 2013 Dec;122(6):487-97. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0430-0. Chromosoma. 2013. PMID: 24022641 Review.
-
Association of yeast RNA polymerase I with a nucleolar substructure active in rRNA synthesis and processing.J Cell Biol. 2000 May 1;149(3):575-90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.575. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10791972 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RNA Polymerase I Transcription in Development, Disease, and Aging.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:51-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012612. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29589958 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-Induced Evolution of the Nucleolus: The Role of Ribosomal Intergenic Spacer (rIGS) Transcripts.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 20;14(10):1333. doi: 10.3390/biom14101333. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of RNA Polymerase I Stability and Function.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(23):5776. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235776. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond ribosome biogenesis: noncoding nucleolar RNAs in physiology and tumor biology.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2274655. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2274655. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 37906621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paralog-Dependent Specialization of Paf1C Subunit, Ctr9, for Sex Chromosome Gene Regulation and Male Germline Differentiation in Drosophila.Genes Cells. 2025 Sep;30(5):e70040. doi: 10.1111/gtc.70040. Genes Cells. 2025. PMID: 40763999 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar detention of NONO shields DNA double-strand breaks from aberrant transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 12;52(6):3050-3068. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38224452 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
