Nanoparticulate cell-free DNA scavenger for treating inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis
- PMID: 36207325
- PMCID: PMC9546917
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33492-6
Nanoparticulate cell-free DNA scavenger for treating inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis
Abstract
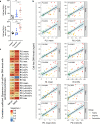
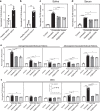
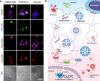
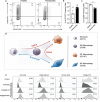
Periodontitis is a common type of inflammatory bone loss and a risk factor for systemic diseases. The pathogenesis of periodontitis involves inflammatory dysregulation, which represents a target for new therapeutic strategies to treat periodontitis. After establishing the correlation of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) level with periodontitis in patient samples, we test the hypothesis that the cfDNA-scavenging approach will benefit periodontitis treatment. We create a nanoparticulate cfDNA scavenger specific for periodontitis by coating selenium-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (SeHANs) with cationic polyamidoamine dendrimers (PAMAM-G3), namely G3@SeHANs, and compare the activities of G3@SeHANs with those of soluble PAMAM-G3 polymer. Both G3@SeHANs and PAMAM-G3 inhibit periodontitis-related proinflammation in vitro by scavenging cfDNA and alleviate inflammatory bone loss in a mouse model of ligature-induced periodontitis. G3@SeHANs also regulate the mononuclear phagocyte system in a periodontitis environment, promoting the M2 over the M1 macrophage phenotype. G3@SeHANs show greater therapeutic effects than PAMAM-G3 in reducing proinflammation and alveolar bone loss in vivo. Our findings demonstrate the importance of cfDNA in periodontitis and the potential for using hydroxyapatite-based nanoparticulate cfDNA scavengers to ameliorate periodontitis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Liwinski, T., Zheng, D. & Elinav, E. The microbiome and cytosolic innate immune receptors. Immunol Rev, 10.1111/imr.12901 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

