Psychometric properties of the Last-7-Day Sedentary Time Questionnaire (SIT-Q-7d): Testing the validity and reliability among general population
- PMID: 36209048
- PMCID: PMC9547410
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-14262-x
Psychometric properties of the Last-7-Day Sedentary Time Questionnaire (SIT-Q-7d): Testing the validity and reliability among general population
Abstract
Backgrounds: Sedentary behavior (SB) is an independent risk factor causing chronic diseases. Previous studies compared sitting time mostly with physical activity. The present study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Last-7-Day Sedentary Time Questionnaire (SIT-Q-7d) in Iran. Moreover, SB was assessed among the study participants.
Methods: The current validity study was conducted among 290 subjects (51.7% males vs. 48.3% females) with a mean age of 34.81 ± 9.63 years in Poldasht, Iran. Sampling was done using simple random sampling and the data were collected using the SIT-Q-7d. To confirm the validity of the questionnaire, forward-backward translation method, content validity, and construct validity were used. Furthermore, temporal stability was calculated by the test-retest method and internal consistency coefficient (ICC).
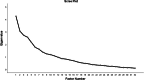
Results: Our results confirmed the content validity of the questionnaire (content validity score: 0.90 and content validity index: 0.80). Using exploratory factor analysis (EFA), seven factors of SB were identified as follows: eating while sitting down, doing domestic affairs, screen time, leisure time, studying books, watching TV, and attending family gatherings. The reliability of the questionnaire was confirmed using Cronbach's alpha (α = 0.7). In addition, temporal stability was confirmed by test-retest method and ICC was 0.9 (95% CI: 83-97).
Conclusion: Our results confirmed that the Persian version of SIT-Q-7d is a reliable and valid tool for assessing SB.
Keywords: Iran; Reliability; SIT-Q-7d questionnaire; Sedentary behavior; Validity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Redevelopment and Examination of the Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Last 7-Day Sedentary Behaviour Questionnaire (SIT-Q-7d-Chi) in Hong Kong Older Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 13;19(10):5958. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19105958. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627497 Free PMC article.
-
Validation study of the Spanish version of the Last-7-d Sedentary Time Questionnaire (SIT-Q-7d-Sp) in young adults.PLoS One. 2019 May 29;14(5):e0217362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217362. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31141542 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of the Persian version of the sedentary behavior questionnaire among office employees.Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2023 Sep;29(3):1101-1106. doi: 10.1080/10803548.2022.2111879. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2023. PMID: 35946579
-
Persian version of the brief Older People's Quality of Life questionnaire (OPQOL-brief): the evaluation of the psychometric properties.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Oct 7;18(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01586-8. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 33028355 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Health Behavior in School-Aged Survey Questionnaire Reliable and Valid in Assessing Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Populations? A Systematic Review.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 28;10:729641. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.729641. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35419332 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Do consumers continue to use O2O food delivery services in the post-pandemic era? Roles of sedentary lifestyle.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 15;9(9):e19131. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19131. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37662809 Free PMC article.
-
Harmonizing measurement tools: examining the concurrent validity of the Daily Activity Behaviors Questionnaire compared to the ActiGraph to assess 24-hour movement behaviors among adults.BMC Public Health. 2024 Dec 30;24(1):3607. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21139-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39736604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pasdar Y, Niazi P, Darbandi M, Khalundi F, Izadi N. Study of physical activity and its effect on body composition and quality of life in female employees of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences in 2013. Scie J Rafsanjan Uni Med Scie. 2015;14(2):99–110.
-
- Momenan, AA, Delshad, Mirmiran, G. Parvin, et al, The rate of inactivity and its related factors in the adult population of Tehran: a study of glucose and lipids in Tehran. Iranian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, a bi-monthly research journal of the Endocrine and Metabolism Research Center, 2012.13(5):493–503.
-
- Organization WH. Physical inactivity: a global public health problem. 2010. https://www.Who.int/dietphysicalactivity/factsheet_inactivity/en/. Part I APPEND, 2012.
-
- Kai Y, Kitano K, Nagamatsu T, Kuchiki T, Onodera Y. Reliability and validity of the Sedentary Lifestyle Questionnaire for Japanese (SLQ-J) Bull Phys Fit Res Inst. 2017;115:23–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical