Changes in R-wave amplitude at implantation are associated with gender and orientation of insertable cardiac monitor: observations from the confirm Rx™ body posture and physical activity study
- PMID: 36209063
- PMCID: PMC9548115
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02752-0
Changes in R-wave amplitude at implantation are associated with gender and orientation of insertable cardiac monitor: observations from the confirm Rx™ body posture and physical activity study
Abstract
Background: Insertable cardiac monitors (ICMs) are small subcutaneously implanted devices that detect changes in R-wave amplitudes (RWAs), effective in arrhythmia-monitoring. Although ICMs have proven to be immensely successful, electrical artefacts are frequent and can lead to misdiagnosis. Thus, there is a growing need to sustain and increase efficacy in detection rates by gaining insight into various patient-specific factors such as body postures and activities.
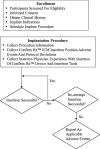
Methods: RWAs were measured in 15 separate postures, including supine, lying on the right-side (RS) or left-side (LS) and sitting, and two separate ICM orientations, immediately after implantation of Confirm Rx™ ICM in 99 patients.
Results: The patients (53 females and 46 males, mean ages 66.62 ± 14.7 and 66.40 ± 12.25 years, respectively) had attenuated RWAs in RS, LS and sitting by ~ 26.4%, ~ 27.8% and ~ 21.2% respectively, compared to supine. Gender-based analysis indicated RWAs in RS (0.32 mV (0.09-1.03 mV), p < 0.0001) and LS (0.37 mV (0.11-1.03 mV), p = 0.004) to be significantly attenuated compared to supine (0.52 mV (0.20-1.03 mV) for female participants. Similar attenuation was not evident for male participants. Further, parasternally oriented ICMs (n = 44), attenuated RWAs in RS (0.37 mV(0.09-1.03 mV), p = 0.05) and LS (0.34 mV (0.11-1.03 mV), p = 0.02) compared to supine (0.48 mV (0.09-1.03 mV). Similar differences were not observed in participants with ICMs in the 45°-relative-to-sternum (n = 46) orientation. When assessing the combined effect of gender and ICM orientation, female participants demonstrated plausible attenuation in RWAs for RS and LS postures compared to supine, an effect not observed in male participants.
Conclusion: This is the first known study depicting the effects on RWA due to body postures and activities immediately post-implantation with an overt impact by gender and orientation of ICM. Future work assessing the cause of gender-based differences in RWAs may be critical.
Trial registration: Clinical Trials, NCT03803969. Registered 15 January 2019 - Retrospectively registered, https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT03803969.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Gender; Insertable cardiac monitor; Posture; R-wave amplitudes; Syncope.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SD, LM and KR are employees of Abbott. All other authors declare No Conflict of Interests for this article.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

