A unilateral robotic knee exoskeleton to assess the role of natural gait assistance in hemiparetic patients
- PMID: 36209096
- PMCID: PMC9548210
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-022-01088-2
A unilateral robotic knee exoskeleton to assess the role of natural gait assistance in hemiparetic patients
Abstract
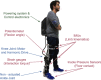
Background: Hemiparetic gait is characterized by strong asymmetries that can severely affect the quality of life of stroke survivors. This type of asymmetry is due to motor deficits in the paretic leg and the resulting compensations in the nonparetic limb. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effect of actively promoting gait symmetry in hemiparetic patients by assessing the behavior of both paretic and nonparetic lower limbs. This paper introduces the design and validation of the REFLEX prototype, a unilateral active knee-ankle-foot orthosis designed and developed to naturally assist the paretic limbs of hemiparetic patients during gait.
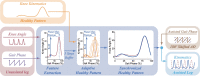
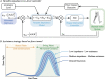
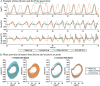
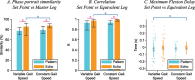
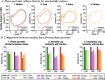
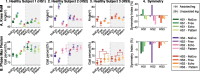
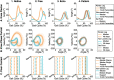
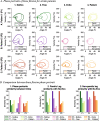
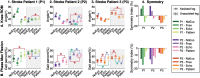
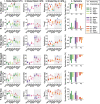
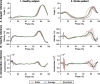
Methods: REFLEX uses an adaptive frequency oscillator to estimate the continuous gait phase of the nonparetic limb. Based on this estimation, the device synchronically assists the paretic leg following two different control strategies: (1) replicating the movement of the nonparetic leg or (2) inducing a healthy gait pattern for the paretic leg. Technical validation of the system was implemented on three healthy subjects, while the effect of the generated assistance was assessed in three stroke patients. The effects of this assistance were evaluated in terms of interlimb symmetry with respect to spatiotemporal gait parameters such as step length or time, as well as the similarity between the joint's motion in both legs.
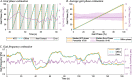
Results: Preliminary results proved the feasibility of the REFLEX prototype to assist gait by reinforcing symmetry. They also pointed out that the assistance of the paretic leg resulted in a decrease in the compensatory strategies developed by the nonparetic limb to achieve a functional gait. Notably, better results were attained when the assistance was provided according to a standard healthy pattern, which initially might suppose a lower symmetry but enabled a healthier evolution of the motion of the nonparetic limb.
Conclusions: This work presents the preliminary validation of the REFLEX prototype, a unilateral knee exoskeleton for gait assistance in hemiparetic patients. The experimental results indicate that assisting the paretic leg of a hemiparetic patient based on the movement of their nonparetic leg is a valuable strategy for reducing the compensatory mechanisms developed by the nonparetic limb.
Keywords: Gait symmetry; Hemiparetic gait; Robotic exoskeleton; Stroke patients; Unilateral assistance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


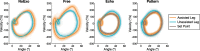
Similar articles
-
Effects of Bilateral Assistance for Hemiparetic Gait Post-Stroke Using a Powered Hip Exoskeleton.Ann Biomed Eng. 2023 Feb;51(2):410-421. doi: 10.1007/s10439-022-03041-9. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 35963920 Free PMC article.
-
Articulated ankle-foot-orthosis improves inter-limb propulsion symmetry during walking adaptability task post-stroke.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2024 Jun;116:106268. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2024.106268. Epub 2024 May 18. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2024. PMID: 38795609
-
Step length asymmetry is representative of compensatory mechanisms used in post-stroke hemiparetic walking.Gait Posture. 2011 Apr;33(4):538-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2011.01.004. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Gait Posture. 2011. PMID: 21316240 Free PMC article.
-
Paretic propulsion as a measure of walking performance and functional motor recovery post-stroke: A review.Gait Posture. 2019 Feb;68:6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.10.027. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Gait Posture. 2019. PMID: 30408710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of adaptive control for stroke lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot based on motion intention recognition.Front Neurorobot. 2023 Jul 3;17:1186175. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1186175. eCollection 2023. Front Neurorobot. 2023. PMID: 37465413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical impedance myography combined with quantitative assessment techniques in paretic muscle of stroke survivors: Insights and challenges.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 16;15:1130230. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1130230. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37020859 Free PMC article.
-
Control strategies used in lower limb exoskeletons for gait rehabilitation after brain injury: a systematic review and analysis of clinical effectiveness.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023 Feb 19;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12984-023-01144-5. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 36805777 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic exoskeleton embodiment in post-stroke hemiparetic patients: an experimental study about the integration of the assistance provided by the REFLEX knee exoskeleton.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 21;13(1):22908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50387-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38129592 Free PMC article.
-
Human-Interface Dynamics of Knee Exoskeletons with Lateral and Anteroposterior Attachment.IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2025 May;2025:648-655. doi: 10.1109/ICORR66766.2025.11062962. IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2025. PMID: 40644288
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

