Retrospective analysis of GnRH-a prolonged protocol for in vitro fertilization in 18,272 cycles in China
- PMID: 36209186
- PMCID: PMC9548105
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-022-01044-7
Retrospective analysis of GnRH-a prolonged protocol for in vitro fertilization in 18,272 cycles in China
Abstract
Background: This large-cohort, retrospective study investigates the relationship between the number of oocytes retrieved and the clinical outcomes for patients receiving the GnRH-a prolonged protocol (mGnRH-a protocol) for fertilization in vitro or intracytoplasmic sperm injection-embryo transfer (IVF/ICSI-ET) treatment.
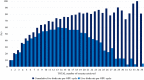
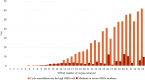
Results: We categorized 18,272 cycles into three groups by the number of oocytes retrieved (1-8, 9-17, and ≥ 18) during IVF with the GnRH-a prolonged protocol at the Reproductive Medical Center of Jiangxi Maternal and Child Health Hospital from January 2014 to December 2018 (excluding oocyte donation cycles), analyzing the associations among oocyte number and live birth rates (LBRs) or cumulative LBRs (CLBRs), as well as the rate of moderate-to-severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). We defined the primary outcome as LBR and the secondary outcome to include the rate of patients at high risk for OHSS. The LBR (with fresh ET) per cycle of oocyte pick-up increased as the number of retrieved oocytes increased from 1 to ~ 8, plateaued between 9 ~ 17, and steadily decreased thereafter. However, the CLBR per cycle continued to increase as the oocyte number increased, as did the incidence of moderate-to-severe OHSS.
Conclusions: Our results show a strong relationship between the number of oocytes retrieved and the CLBR following IVF treatment. The balance between treatment success and the risk of complications, especially OHSS, should be investigated further. We recommend a fresh-ET strategy for the GnRH-a prolonged protocol because the endometrial receptivity in the fresh cycles was better than those in the frozen cycles.
Keywords: GnRH-a prolonged protocol; In vitro fertilization; Live birth rate; OHSS; Oocyte retrieval.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Cumulative live birth rates per oocytes retrieved cycle: evaluation of clinical outcomes of IVF/ICSI].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Mar 25;53(3):160-166. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2018.03.004. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29609229 Chinese.
-
The depot GnRH agonist protocol improves the live birth rate per fresh embryo transfer cycle, but not the cumulative live birth rate in normal responders: a randomized controlled trial and molecular mechanism study.Hum Reprod. 2020 Jun 1;35(6):1306-1318. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa086. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32478400
-
Cumulative live birth rates after one ART cycle including all subsequent frozen-thaw cycles in 1050 women: secondary outcome of an RCT comparing GnRH-antagonist and GnRH-agonist protocols.Hum Reprod. 2017 Mar 1;32(3):556-567. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew358. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28130435 Clinical Trial.
-
Ovarian stimulation for freeze-all IVF cycles: a systematic review.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Jan 1;26(1):118-135. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz037. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 31867625
-
Comparison the effects of progestin-primed ovarian stimulation (PPOS) protocol and GnRH-a long protocol in patients with normal ovarian reserve function.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2023 Dec;39(1):2217263. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2023.2217263. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37236243 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and externally validated prediction model of individualization of FSH starting dose in the depot GnRH agonist protocol for the early follicular phase.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 27;16:1542736. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1542736. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40213105 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting personalized cumulative live birth rate after a complete in vitro fertilization cycle: an analysis of 32,306 treatment cycles in China.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Jun 7;22(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01237-3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38849798 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of dual trigger (GnRH agonist + HCG) versus HCG alone in patients with high ovarian response.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):6668-6678. doi: 10.62347/QKPV5157. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39678590 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources