Modification and application of highly active alkaline pectin lyase
- PMID: 36210372
- PMCID: PMC9548460
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-022-01472-0
Modification and application of highly active alkaline pectin lyase
Abstract
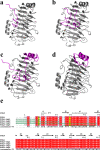
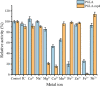
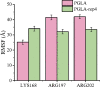
Alkaline pectate lyase has developmental prospects in the textile, pulp, paper, and food industries. In this study, we selected BacPelA, the pectin lyase with the highest expression activity from Bacillus clausii, modified and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Through fragment replacement, the catalytic activity of the enzyme was significantly improved. The optimum pH and temperature of the modified pectin lyase (PGLA-rep4) were 11.0 and 70 °C, respectively. It also exhibited a superior ability to cleave methylated pectin. The enzyme activity of PGLA-rep4, measured at 235 nm with 0.2% apple pectin as the substrate, was 554.0 U/mL, and the specific enzyme activity after purification using a nickel column was 822.9 U/mg. After approximately 20 ns of molecular dynamics simulation, the structure of the pectin lyase PGLA-rep4 tended to be stable. The root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) values at the key catalytically active site, LYS168, were higher than those of the wildtype PGLA. In addition, PGLA-rep4 was relatively stable in the presence of metal ions. PGLA-rep4 has good enzymatic properties and activities and maintains a high pH and temperature. This study provides a successful strategy for enhancing the catalytic activity of PGLA-rep4, making it the ultimate candidate for degumming and various uses in the pulp, paper, and textile industries.
Keywords: Alkaline pectin lyase; Enzymatic activity; Fragment replacement; Molecular dynamics simulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Flow-cytometric cell sorting coupled with UV mutagenesis for improving pectin lyase expression.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 31;11:1251342. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1251342. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37720319 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, evaluation, and high-level expression of a thermo-alkaline pectate lyase from alkaliphilic Bacillus clausii with potential in ramie degumming.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 May;101(9):3663-3676. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8110-2. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28184988
-
Structure of an Alkaline Pectate Lyase and Rational Engineering with Improved Thermo-Alkaline Stability for Efficient Ramie Degumming.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):538. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010538. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613981 Free PMC article.
-
Pectinolytic lyases: a comprehensive review of sources, category, property, structure, and catalytic mechanism of pectate lyases and pectin lyases.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021 Aug 23;8(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40643-021-00432-z. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021. PMID: 38650254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins and features of pectate lyases and their applications in industry.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Sep;104(17):7247-7260. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10769-8. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32666183 Review.
Cited by
-
Improvement of optimum pH and specific activity of pectate lyase from Bacillus RN.1 using loop replacement.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 4;11:1242123. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1242123. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37469444 Free PMC article.
-
Flow-cytometric cell sorting coupled with UV mutagenesis for improving pectin lyase expression.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 31;11:1251342. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1251342. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37720319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adetunji LR, Adekunle A, Orsat V, Raghavan V. Advances in the pectin production process using novel extraction techniques: a review. Food Hydrocolloids. 2017;62:239–250. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.08.015. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharyya R, Mukhopadhyay D, Nagarakshita VK, Bhattacharya S, Das A. Thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant acid pectinase from Aspergillus terreus FP6: purification, characterization and evaluation of its phytopigment extraction potential. 3 Biotech. 2021;11(11):487. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-03033-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camarero S, Garcia O, Vidal T, Colom J, Rio JCD, Gutierrez A, Gras JM, Monje R, Martinez MJ, Martinez AT. Efficient bleaching of non-wood high-quality paper pulp using laccase-mediator system. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2003;35(2):113–120. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.10.019. - DOI
-
- Cerreti M, Markosova K, Esti M, Rosenberg M, Rebros M. Immobilisation of pectinases into PVA gel for fruit juice application. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2017;52(2):531–539. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13309. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2019YFC1905902/the National Key Research and Development Plan of China
- 2019YFC1905900/Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program
- 2020CXGC010603/Research and Development Plan in Shandong Province
- 2021ZDSYS10/Research and Development Plan in Shandong Province
- 2022JBZ01-06/Key innovation Project of Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

