Correlation between molar activity, injection mass and uptake of the PARP targeting radiotracer [18F]olaparib in mouse models of glioma
- PMID: 36210377
- PMCID: PMC9548459
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-022-00940-9
Correlation between molar activity, injection mass and uptake of the PARP targeting radiotracer [18F]olaparib in mouse models of glioma
Abstract
Purpose: Radiopharmaceuticals targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) have emerged as promising agents for cancer diagnosis and therapy. PARP enzymes are expressed in both cancerous and normal tissue. Hence, the injected mass, molar activity and potential pharmacological effects are important considerations for the use of radiolabelled PARP inhibitors for diagnostic and radionuclide therapeutic applications. Here, we performed a systematic evaluation by varying the molar activity of [18F]olaparib and the injected mass of [TotalF]olaparib to investigate the effects on tumour and normal tissue uptake in two subcutaneous human glioblastoma xenograft models.
Methods: [18F]Olaparib uptake was evaluated in the human glioblastoma models: in vitro on U251MG and U87MG cell lines, and in vivo on tumour xenograft-bearing mice, after administration of [TotalF]olaparib (varying injected mass: 0.04-8.0 µg, and molar activity: 1-320 GBq/μmol).
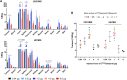
Results: Selective uptake of [18F]olaparib was demonstrated in both models. Tumour uptake was found to be dependent on the injected mass of [TotalF]olaparib (µg) but not the molar activity. An injected mass of 1 μg resulted in the highest tumour uptake (up to 6.9 ± 1.3%ID/g), independent of the molar activity. In comparison, both the lower and higher injected masses of [TotalF]olaparib resulted in lower relative tumour uptake (%ID/g; P < 0.05). Ex vivo analysis of U87MG xenograft sections showed that the heterogeneity in [18F]olaparib intratumoural uptake correlated with PARP1 expression. Substantial upregulation of PARP1-3 expression was observed after administration of [TotalF]olaparib (> 0.5 µg).
Conclusion: Our findings show that the injected mass of [TotalF]olaparib has significant effects on tumour uptake. Moderate injected masses of PARP inhibitor-derived radiopharmaceuticals may lead to improved relative tumour uptake and tumour-to-background ratio for cancer diagnosis and radionuclide therapy.
Keywords: Glioblastoma; Olaparib; PARP; PET; [18F]olaparib.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[18F]AZD2461, an Insight on Difference in PARP Binding Profiles for DNA Damage Response PET Imaging.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Oct;22(5):1226-1234. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01497-6. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 32342268 Free PMC article.
-
PET Imaging of PARP Expression Using 18F-Olaparib.J Nucl Med. 2019 Apr;60(4):504-510. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.213223. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30389822 Free PMC article.
-
Solid phase radiosynthesis of an olaparib derivative using 4-[18F] fluorobenzoic acid and in vivo evaluation in breast and prostate cancer xenograft models for PARP-1 expression.Nucl Med Biol. 2022 Nov-Dec;114-115:65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2022.09.002. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Nucl Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36193598 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination PARP Inhibitor Olaparib With Temozolomide in an Experimental Glioblastoma Model.In Vivo. 2021 Jul-Aug;35(4):2015-2023. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12470. In Vivo. 2021. PMID: 34182476 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging PARP with [18F]rucaparib in pancreatic cancer models.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Sep;49(11):3668-3678. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05835-4. Epub 2022 May 26. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35614267 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aspects and prospects of preclinical theranostic radiopharmaceutical development.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 7;14(17):6446-6470. doi: 10.7150/thno.100339. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-targeted PET imaging in non-oncology application: a pilot study in preclinical models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Feb 20;14(1):41-47. doi: 10.62347/WTKQ3953. eCollection 2024. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38500745 Free PMC article.
-
[18F]F-Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Radiotracers for Imaging PARP Expression and Their Potential Clinical Applications in Oncology.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 11;13(12):3426. doi: 10.3390/jcm13123426. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38929955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quinazoline-2,4(1 H,3 H)-dione Scaffold for development of a novel PARP-targeting PET probe for tumor imaging.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Nov;51(13):3840-3853. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06843-2. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39012502
-
Towards Effective Treatment of Glioblastoma: The Role of Combination Therapies and the Potential of Phytotherapy and Micotherapy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 19;46(12):14324-14350. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120859. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bowden GD, Stotz S, Kinzler J, et al. DoE optimization empowers the automated preparation of enantiomerically pure [18F] talazoparib and its in vivo evaluation as a PARP radiotracer. 2021. 10.26434/chemrxiv.14587401.v1 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

