Unrelated cord blood transplantation vs. HLA-matched sibling transplantation for adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in complete remission: superior OS for patients with long-term survival
- PMID: 36210439
- PMCID: PMC9549614
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03186-3
Unrelated cord blood transplantation vs. HLA-matched sibling transplantation for adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in complete remission: superior OS for patients with long-term survival
Abstract
Background: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is an important curative therapy for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). For patients who lack a human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched sibling donor, unrelated cord blood (UCB) is an alternative graft option. Previous studies have focused mainly on all T- and B-cell ALL (B-ALL) patients, while data related specifically to adult B-ALL patients after UCB transplantation (UCBT) are scarce.
Methods: We retrospectively compared the outcomes of UCBT and HLA-matched sibling transplantation (MST) in the treatment of adult B-ALL patients in complete remission (CR) at our center. From June 2006 to December 2020, 156 adult B-ALL patients who achieved CR before transplantation were enrolled. The main clinical outcomes of UCBT and MST were analyzed.
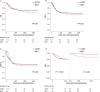
Results: Hematopoietic recovery was significantly faster in MST recipients than in UCBT recipients. Higher incidences of grades II-IV and III-IV acute graft-versus host disease (aGVHD) were found in UCBT recipients (P < 0.001 and = 0.03), while a lower incidence of extensive chronic GVHD (cGVHD) was found in UCBT recipients (P < 0.001). The cumulative incidences of 2-year non-relapse mortality (NRM), 2-year relapse, 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) and 5-year GVHD-free relapse-free survival (GRFS) were comparable between MST and UCBT recipients. The overall survival (OS) during the first 700 days was similar between the MST and UCBT groups, while the OS of patients with a survival time of more than 700 days in the UCBT group was better than that in the MST group according to multivariate analysis (P = 0.03).
Conclusions: Our study shows that when treating adult B-ALL patients in CR, UCBT can achieve comparable effects as MST, may provide superior OS for patients with long-term survival, and should be considered a good alternative.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Matched sibling transplantation; Unrelated cord blood transplantation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gokbuget N, Hoelzer D, Arnold R, Böhme A, Bartram CR, Freund M, Ganser A, Kneba M, Langer W, Lipp T, et al. Treatment of adult all according to protocols of the German multicenter study group for adult all (Gmall) Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14(6):1307–1325. doi: 10.1016/S0889-8588(05)70188-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Josep-María Ribera AO, Concepción Bethencourt, Ricardo Parody, Jesús-María Hernández-Rivas, María-José Moreno, Eloy del Potro, Mar Torm, Concepción Rivas, Joan Besalduch, Miguel-Angel Sanz, Juan-José Ortega, PETHEMA Group, Spain: Comparison of intensive chemotherapy, allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation as post-remission treatment for adult patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Results of the PETHEMA ALL-93 trial. Haematologica. (2005); 90(10): 1346–1356. - PubMed
-
- Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK, Burnett AK, Chopra R, Wiernik PH, Foroni L, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the international all trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993) Blood. 2008;111(4):1827–1833. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-116582. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

