[microRNA let-7g-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells by targeting HMGB2]
- PMID: 36210706
- PMCID: PMC9550544
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.09.09
[microRNA let-7g-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells by targeting HMGB2]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism by which microRNA let-7g-3p regulates biological behaviors of bladder cancer cells.
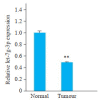
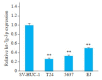
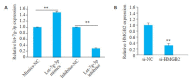
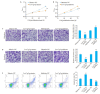
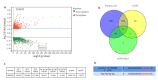
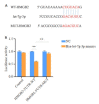
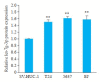
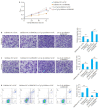
Methods: The expression levels of let-7g-3p in bladder cancer and adjacent tissues, normal bladder epithelial cells (HUC cells) and bladder cancer cells (T24, 5637 and EJ cells) were detected using qRT- PCR. T24 cells were transfected with let-7g-3p mimic or inhibitor, and the changes in cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were examined. Transcriptome sequencing was carried out in cells overexpressing let-7g-3p, and the results of bioinformatics analysis, double luciferase reporter gene assay, qRT-PCR and Western blotting confirmed that HMGB2 gene was the target gene of let-7g-3p. The expression of HMGB2 was examined in HUC, T24, 5637 and EJ cells, and in cells with HMGB2 knockdown, the effect of let-7g-3p knockdown on the biological behaviors were observed.
Results: qRT-qPCR confirmed that let-7g-3p expression was significantly lower in bladder cancer tissues and cells (P < 0.01). Overexpression of let-7g-3p inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and promoted cell apoptosis, while let-7g-3p knock-down produced the opposite effects. Bioinformatics and transcriptome sequencing results showed that HMGB2 was the key molecule that mediate the effect of let-7g-3p on bladder cancer cells. Luciferase reporter gene assay, qRT-PCR and Western blotting all confirmed that HMGB2 was negatively regulated by let-7g-3p (P < 0.01). Knocking down HMGB2 could partially reverse the effect of let-7g-3p knockdown on the biological behaviors of the bladder cancer cells.
Conclusion: The microRNA let-7g-3p can inhibit the biological behavior of bladder cancer cells by negatively regulating HMGB2 gene.
目的: 探讨MiR-let-7g-3p靶向HMGB2对膀胱癌细胞生物学行为的影响及其分子机制。
方法: 通过qRT-PCR检测膀胱癌组织和癌旁组织以及正常尿路上皮细胞SV-HUC-1和膀胱癌细胞(T24、5637和EJ)中let-7g-3p的表达水平;通过转染过表达或敲低T24细胞let-7g-3p表达,检测细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭、和凋亡等变化;对过表达let-7g-3p的细胞进行转录组测序,结合生物信息学分析,通过双荧光素酶报告实验、qRT-PCR和Western-blot分析let-7g-3p靶向负性调控HMGB2基因;qRT-PCR检测正常尿路上细胞和膀胱癌细胞(T24、5637和EJ)中HMGB2的表达水平,并且在敲低HMGB2的细胞株中,敲低let-7g-3p,检测细胞生物学行为改变。
结果: qRT-qPCR证实let-7g-3p在膀胱癌组织和细胞表达明显下调(P < 0.01);过表达let-7g-3p可抑制细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,促进细胞凋亡(P < 0.01);相反,敲减let-7g-3p表达可促进细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,抑制细胞凋亡(P < 0.01)。生物信息学和转录组测序结果显示,HMGB2是let-7g-3p作用于膀胱癌细胞的关键分子;双荧光素酶报告实验、qRT-PCR和Western blot显示,HMGB2受let-7g-3p的负性调控;HMGB2膀胱癌细胞中表达水平均明显上调(P < 0.01),敲低HMGB2可部分逆转敲低let-7g-3p对膀胱癌细胞生长的促进作用。
结论: MiRNA-let-7g-3p通过靶向负性调控HMGB2基因抑制膀胱癌细胞的生物行为。
Keywords: HMGB2; bladder cancer; let-7g-3p.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA KTN1-AS1 promotes progression in pancreatic cancer through regulating microRNA-23b-3p/high-mobility group box 2 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Aug 30;13(16):20820-20835. doi: 10.18632/aging.203481. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34461605 Free PMC article.
-
[miR-let-7c-5p inhibits invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells by targeting HMGA2].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Jul 20;41(7):1022-1029. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.07.08. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34308851 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
miR-325-3p Overexpression Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Bladder Cancer Cells by Regulating MT3.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 8;26:e920331. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920331. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32512576 Free PMC article.
-
[Mir-29c-3p targeting TUG1 affects migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by regulating CAPN7 expression].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Sep 30;40(9):1325-1331. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.09.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32990242 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
miR-148a-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer via regulating the expression of ROCK-1.PeerJ. 2022 Jan 26;10:e12724. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12724. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35127282 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive and clinicopathological importance of HMGB2 in various carcinomas: a meta and bioinformatic approach.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 31;15(1):11003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95505-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40164660 Free PMC article.
-
[High expression of miR-204-5p promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells by negatively regulating RAB22A].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Nov 20;44(11):2235-2242. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.21. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39623280 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
LINC00534 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting the miR-139-5p/HMGB2 axis.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 2;16(1):655. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02483-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40314851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pugashetti N, Alibhai SMH, Yap SA. Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: review of diagnosis and management. J Curr Clin Care. 2015;105:540–50.
-
- Wang H, Ke C, Ma X, et al. microRNA-92 promotes invasion and chemoresistance by targeting GSK3β and activating Wnt signaling in bladder cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;2016(9):517–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
