Mechanism investigation and experiment validation of capsaicin on uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
- PMID: 36210802
- PMCID: PMC9532580
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.953874
Mechanism investigation and experiment validation of capsaicin on uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
Abstract
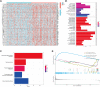
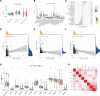
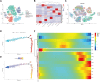
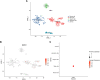
Background: Using bioinformatics analysis and experimental operations, we intend to analyze the potential mechanism of action of capsaicin target gene GATA1 in the treatment of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC) and develop a prognostic model for the disease to validate this model. Methods: By obtaining capsaicin and UCEC-related DR-DEGs, the prognosis-related gene GATA1 was screened. The survival analysis was conducted via establishing high and low expression groups of GATA1. Whether the GATA1 could be an independent prognostic factor for UCEC, it was also validated. The therapeutic mechanism of capsaicin-related genes in UCEC was further investigated using enrichment analysis and immune methods as well as in combination with single-cell sequencing data. Finally, it was validated by cell experiments. Results: GATA1, a high-risk gene associated with prognosis, was obtained by screening. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the survival of the high expression group was lower than that of low expression group. ROC curves showed that the prediction effect of the model was good and stable (1-year area under curve (AUC): 0.601; 2-years AUC: 0.575; 3-years AUC: 0.610). Independent prognosis analysis showed that the GATA1 can serve as an independent prognostic factor for UCEC. Enrichment analysis showed that "neuroactive Ligand - receptor interaction and TYPE I DIABETES MELLITUS" had a significant enrichment effect. Single-cell sequencing showed that the GATA1 was significantly expressed in mast cells. Cell experiments showed that the capsaicin significantly reduced the UCEC cell activity and migration ability, as well as inhibited the expression of GATA1. Conclusion: This study suggests that the capsaicin has potential value and application prospect in the treatment of UCEC. It provides new genetic markers for the prognosis of UCEC patients.
Keywords: UCEC; bioinformatics; capsaicin; experiment validation; mechanism investigation.
Copyright © 2022 Lin, Sui, Jiao, Chen, Zhang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of a prognostic model of luteolin for endometrial carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):2122-2139. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056832 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and validation of potential markers associated with uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma and polycystic ovary syndrome based on bioinformatics methods.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jun 9;10:1192313. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1192313. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37363398 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hub Genes Correlated With Poor Prognosis for Patients With Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 19;11:766947. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.766947. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34868993 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation reveals fatty acid metabolism-related prognostic signature and immune responses for uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 9;12:1030246. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1030246. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439473 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL9 correlates with antitumor immunity and is predictive of a favorable prognosis in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 8;13:1077780. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1077780. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845675 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the role of tumor-associated ALOX5+ mast cells with transformative function in cervical cancer progression via single-cell RNA sequencing.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1434450. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434450. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39224598 Free PMC article.
-
A new perspective on macrophage-targeted drug research: the potential of KDELR2 in bladder cancer immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 3;15:1485109. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485109. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39691708 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell insights into HNSCC tumor heterogeneity and programmed cell death pathways.Transl Oncol. 2025 Apr;54:102341. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102341. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40068384 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA Protects Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Inhibiting the HAS2/FGF9 Axis.Cardiol Res Pract. 2024 Nov 13;2024:2581638. doi: 10.1155/2024/2581638. eCollection 2024. Cardiol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39568660 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the endothelial cell landscape in meningioma: single-cell insights into PLVAP+ subpopulations and their role in tumor angiogenesis.Front Immunol. 2025 May 27;16:1591125. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1591125. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40496867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2021). Cancer statistics for USA. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/endometrial-cancer/about/key-statistics.html .
-
- Ammendola M., Sacco R., Sammarco G., Donato G., Montemurro S., Ruggieri E., et al. (2014). Correlation between serum tryptase, mast cells positive to tryptase and microvascular density in colo-rectal cancer patients: Possible biological-clinical significance. PLoS One 9 (6), e99512. 10.1371/journal.pone.0099512 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen M. D., Kamper P., Nielsen P. S., Bendix K., Riber-Hansen R., Steiniche T., et al. (2016). Tumour-associated mast cells in classical hodgkin's lymphoma: Correlation with histological subtype, other tumour-infiltrating inflammatory cell subsets and outcome. Eur. J. Haematol. 96 (3), 252–259. 10.1111/ejh.12583 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

