Immunogenicity of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in hemodialysis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36210877
- PMCID: PMC9528953
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.874
Immunogenicity of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in hemodialysis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: Vaccine response is a concern in hemodialysis patients. Given that hemodialysis patients were not included in clinical trials, we aimed to synthesize the available evidence on the immunogenicity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccines in hemodialysis patients.
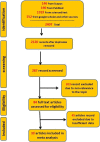
Methods: We searched Scopus, PubMed, Sciencedirect, and finally google scholar databases for studies on COVID-19 mRNA-vaccines immunogenicity in hemodialysis patients up to December 1, 2021. Eligible articles measured antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike or Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody (S/RBD) postimmunization with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. The immunogenicity of the vaccine was evaluated using seroconversion rates measured between 21 and 30 days after the first immunization and between 14 and 36 days post the second dose. We included studies including participants without a history of COVID-19 before vaccination. Healthy controls or health-care workers served as the control groups. After selecting eligible articles, the data were finally extracted from included articles. We used a random effects model to estimate the pooled seroconversion rate after COVID-19 mRNA vaccine administration. We assessed the heterogeneity between studies with the I 2 statistical index.
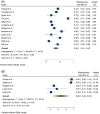
Result: We selected 39 eligible citations comprising 806 cases and 336 controls for the first dose and 6314 cases and 927 controls for the second dose for statistical analysis. After the first dose of mRNA vaccines, the seroconversion rate was 36% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.24-0.47) and 68% (95% CI: 0.45-0.91) in hemodialysis patients and the control group, respectively. While seroconversion rate after the second dose of mRNA vaccines was 86% (95% CI: 0.81-0.91) and 100% (95% CI: 1.00-1.00) in hemodialysis patients and the control group, respectively.
Conclusion: Although the immune response of hemodialysis patients to the second dose of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine is very promising, the seroconversion rate of dialysis patients is lower than healthy controls. Periodically assessment of antibody levels of hemodialysis patients at short intervals is recommended.
Keywords: COVID‐19 mRNA vaccines; SARS‐CoV‐2; chronic kidney disease; hemodialysis; the seroconversion rate; vaccine immunogenicity.
© 2022 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response to the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Sep 1;4(9):e2123622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.23622. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34473256 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine (ZF2001) in healthy children and adolescents aged 3-17 years in China: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial and an open-label, non-randomised, non-inferiority, phase 2 trial.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023 Apr;7(4):269-279. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00376-5. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023. PMID: 36803632 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine CS-2034: A randomized, double-blind, dose-exploration, placebo-controlled multicenter Phase I clinical trial in healthy Chinese adults.J Infect. 2023 Dec;87(6):556-570. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 28. J Infect. 2023. PMID: 37898410 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of covid-19 vaccines in immunocompromised patients: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ. 2022 Mar 2;376:e068632. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-068632. BMJ. 2022. PMID: 35236664 Free PMC article.
-
Seroconversion rate after primary vaccination with two doses of BNT162b2 versus mRNA-1273 in solid organ transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Jul 26;37(8):1566-1575. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac174. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35544087 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reverse vaccinology approaches to design a potent multiepitope vaccine against the HIV whole genome: immunoinformatic, bioinformatics, and molecular dynamics approaches.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):873. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09775-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39198721 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccination Among Patients Receiving Maintenance Renal Replacement Therapy: Immune Response, Real-World Effectiveness, and Implications for the Future.J Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 4;228(Suppl 1):S46-S54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad162. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37539761 Free PMC article.
-
B and T cell responses to the 3rd and 4th dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine in dialysis patients.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2292376. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2292376. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38191151 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccine Antibody Response in a Single-Center Urban Hemodialysis Unit.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 18;11(7):1252. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071252. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37515067 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal COVID-19 infection and the fetus: Immunological and neurological perspectives.New Microbes New Infect. 2023 Jun;53:101135. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101135. Epub 2023 Apr 27. New Microbes New Infect. 2023. PMID: 37143853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

