Mechanistic Insights into Iron-Catalyzed C-H Bond Activation and C-C Coupling
- PMID: 36210909
- PMCID: PMC9542290
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.1c00211
Mechanistic Insights into Iron-Catalyzed C-H Bond Activation and C-C Coupling
Abstract
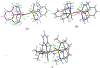
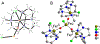
Iron-catalyzed C-C coupling reactions of pyrrole provide a unique alternative to the traditional Pd-catalyzed counterpart. However, many details regarding the actual mechanism remain unknown. A series of macrocyclic iron(III) complexes were used to evaluate specifics related to the role of O2, radicals, and μ-oxodiiron-complex participation in the catalytic cycle. It was determined that the mononuclear tetra-azamacrocyclic complex is a true catalyst and not a stoichiometric reagent, while more than one equivalent of a sacrificial oxidant is needed. Furthermore, the reaction does not proceed through an organic radical pathway. μ-Oxodiiron complexes are not involved in the main catalytic pathway, and the dimers are, in fact, off-cycle species that decrease catalytic efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


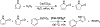
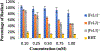


References
-
- Miyaura N; Suzuki A Stereoselective synthesis of arylated (E)-alkenes by the reaction of alk-1-enylboranes with aryl halides in the presence of palladium catalyst. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun 1979, 19, 866–867.
-
- Miyaura N; Yamada K; Suzuki A A new stereospecific crosscoupling by the palladium-catalyzed reaction of 1-alkenylboranes with 1-alkenyl or 1-alkynyl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3437–3440.
-
- Wu G; Jacobi von Wangelin A Iron-catalysed Suzuki biaryl couplings. Nat. Catal 2018, 1, 377–378.
-
- Shang R; Ilies L; Nakamura E Iron-Catalyzed C−H Bond Activation. Chem. Rev 2017, 117, 9086–9139. - PubMed
-
- Andrews NC Disorders of Iron Metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med 1999, 341, 1986–1995. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
