Bilateral sterile subdural effusion in Kawasaki disease-A case report
- PMID: 36210955
- PMCID: PMC9535611
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.990544
Bilateral sterile subdural effusion in Kawasaki disease-A case report
Abstract
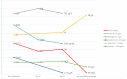
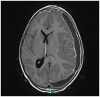
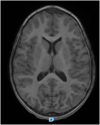
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile condition that causes a self-limiting medium vessel systemic vasculitis and whose pathophysiological pathways are still not completely understood. Coronary arteries are the most affected, but inflammation can develop in all medium-sized arteries, with various organs and tissues being involved. Kawasaki disease-related neurological involvement varies in terms of clinical expression and severity. Herein, we describe an unusual neurological complication of Kawasaki disease in a 5-year-old girl. The progression of the disease was biphasic. Kawasaki disease was diagnosed on the 8th day after symptoms onset and treated by intravenous immunoglobulins, with prompt clinical regression but a less favorable biological response (persistent inflammation with hypoalbuminemia). Two weeks later, headaches and lethargy developed, and a bilateral subdural collection was identified on cerebral imaging. Subsequently, her progress was uneventful, with no residual coronary abnormalities and complete resorption of the subdural collection. Bilateral subdural collection, exceptionally reported, could be discussed as a clinical expression of systemic inflammatory vasculitis that characterizes Kawasaki disease.
Keywords: Kawasaki disease; aseptic meningitis; inflammation; medium vessel vasculitis; subdural collection.
Copyright © 2022 Nicolescu, Duperril and Stephan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tizard EJ. Complications of Kawasaki disease. Curr Pediatr. (2005) 15:62–8. 10.1016/j.cupe.2004.09.002 - DOI
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. . Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. (2004) 114:1708–33. 10.1542/peds.2004-2182 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, et al. . Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American heart association. Circulation. (2017) 135:e927–99. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000484 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

