Diesel-Biodiesel-Water Fuel Nanoemulsions for Direct Injection and Indirect Injection Diesel Engines: Performance and Emission Characteristics
- PMID: 36211034
- PMCID: PMC9535712
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03553
Diesel-Biodiesel-Water Fuel Nanoemulsions for Direct Injection and Indirect Injection Diesel Engines: Performance and Emission Characteristics
Abstract
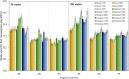
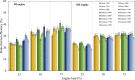
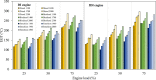
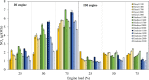
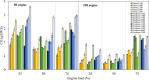
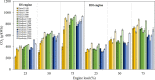
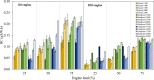
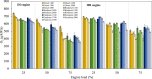
An experimental research is assessed to examine the engine performance and exhaust emissions of direct injection (DI) and indirect injection diesel (IDI) engines fueled with petroleum diesel, biodiesel, and nanoemulsion fuel. The nanoemulsion fuel was produced using a hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. These three fuels were used to study the exhaust emissions, brake power, brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC), brake thermal efficiency (BTE), and exhaust gas temperature at engine speeds ranging from 1100, 1400, 1700, 2000, and 2300 rpm with engine loads of 25, 50, and 75%. Furthermore, three fuels were burned in two types of combustion engines such as DI and IDI diesel engines under identical conditions. The finding showed that using DI and IDI engines influenced the magnitude of emissions as well as the performance with different speeds and loads. By comparing the performance of DI and IDI engines at a maximum engine load of 75%, the most concerning parameter among the efficiency of an engine of BTE of diesel, biodiesel, and nanoemulsion fuel from the DI engine was higher at 24.19, 24.83, and 20.76%, respectively, than that of the IDI engine at 2300 rpm engine speed. At the maximum load and speed of engines, the BSFC of diesel, biodiesel, and nanoemulsion fuel in the DI engine were 4.44, 23.73, and 20% lower than in the IDI engine, respectively. Emission results of the DI and IDI engines were analyzed at 75% load and 2300 rpm speed. The results demonstrated that emissions of NO x from nanoemulsion fuel from the IDI engine was significantly reduced by 82.46% when the values were compared to the DI engine. In terms of CO emissions, the IDI engine emits significantly less than the DI diesel engine. The CO emissions of diesel, biodiesel, and nanoemulsion fuel in the IDI engine were 69.02, 28.95, and 48.75% lower than those in the DI engine, respectively. The studies conclude that the emissions from IDI engines clearly show that pollution from exhaust emissions can be reduced to a low level compared to the DI engine. However, when high-performance engines are considered, the DI engine is recommended rather than the IDI engine.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Diesel-Biodiesel-Ethanol-TiO2 Nanoparticle Blended Fuels on the Performance and Emissions of a Direct Injection Diesel Engine.ACS Omega. 2025 Apr 24;10(17):17337-17352. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10500. eCollection 2025 May 6. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40352481 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Blended Diesel-Biodiesel Fuel on Emissions of a Common Rail Direct Injection Diesel Engine with Different Exhaust Gas Recirculation Rates.ACS Omega. 2024 May 1;9(19):20906-20918. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10125. eCollection 2024 May 14. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38764650 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the performance and gas emissions of a tractor diesel engine using blended fuel diesel and biodiesel to determine the best loading stages.Sci Rep. 2021 May 7;11(1):9811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89287-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33963237 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing marine diesel engine compatibility with sustainable fuels: Key factors and adjustments.Mar Pollut Bull. 2025 Jun;215:117836. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2025.117836. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Mar Pollut Bull. 2025. PMID: 40132479 Review.
-
Aspects of an experimental study of hydrogen use at automotive diesel engine.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 20;9(3):e13889. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13889. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36895365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ANN-ANFIS model for optimising methylic composite biodiesel from neem and castor oil and predicting emissions of the biodiesel blend.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 15;15(1):5638. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88901-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39955378 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Diesel-Biodiesel-Ethanol-TiO2 Nanoparticle Blended Fuels on the Performance and Emissions of a Direct Injection Diesel Engine.ACS Omega. 2025 Apr 24;10(17):17337-17352. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10500. eCollection 2025 May 6. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40352481 Free PMC article.
-
Upgrading Pyrolysis Bio-Oil through Esterification Process and Assessing the Performance and Emissions of Diesel-Biodiesel-Esterified Pyrolysis Bio-Oil Blends in Direct Injection Diesel Engines.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 13;8(47):44586-44600. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05007. eCollection 2023 Nov 28. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38046294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhen X.; Wang Y.; Liu D. Bio–butanol as a new generation of clean alternative fuel for SI (spark ignition) and CI (compression ignition) engines. Renewable Energy 2020, 147, 2494–2521. 10.1016/j.renene.2019.10.119. - DOI
-
- Landi G.; Di Sarli V.; Lisi L. A numerical investigation of the combined effects of initial temperature and catalyst activity on the dynamics of soot combustion in a catalytic diesel particulate filter. Top. Catal. 2021, 64, 270–287. 10.1007/s11244-020-01386-w. - DOI
-
- Di Sarli V.; Landi G.; Di Benedetto A.; Lisi L. Synergy between ceria and metals (Ag or Cu) in catalytic diesel particulate filters: Effect of the metal content and of the preparation method on the regeneration performance. Top. Catal. 2021, 64, 256–269. 10.1007/s11244-020-01384-y. - DOI
-
- Ghaffarpasand O.; Beddows D. C. S.; Ropkins K.; Pope F. D. Real–world assessment of vehicle air pollutant emissions subset by vehicle type, fuel and EURO class: New findings from the recent UK EDAR field campaigns, and implications for emissions restricted zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 13941610.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139416. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duarte Souza Alvarenga Santos N.; Rückert Roso V.; Teixeira Malaquias A. C.; Coelho Baêta J. G. Internal combustion engines and biofuels: Examining why this robust combination should not be ignored for future sustainable transportation. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 11129210.1016/j.rser.2021.111292. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
