New insights into cataract surgery in patients with uveitis: A detailed review of the current literature
- PMID: 36211311
- PMCID: PMC9535913
- DOI: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_147_21
New insights into cataract surgery in patients with uveitis: A detailed review of the current literature
Abstract
Cataract is a common cause of visual impairment in uveitic eyes. The management of cataract in patients with uveitis is often challenging due to pre-existing ocular comorbidities that may limit the visual outcomes. A meticulous preoperative ophthalmic evaluation is needed to assess the concomitant ocular pathologies with special emphasis on the status of the macula and optic nerve. Preoperative control of inflammation for at least 3 months before surgery is a key prognostic factor for successful surgical outcomes. Perioperative use of systemic and topical corticosteroids along with other immunosuppressive medications is crucial to decrease the risk of postoperative inflammation and cystoid macular edema (CME). Phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation is the surgical option of choice for most patients with uveitic cataract. Uveitic cataracts are typically complicated by the presence of posterior synechiae and poor pupil dilation, necessitating manual stretching maneuvers or pupil expansion devices to dilate the pupil intraoperatively. Patients must be closely monitored for postoperative complications such as excessive postoperative inflammation, CME, raised intraocular pressure, hypotony, and other complications. Good outcomes can be achieved in uveitic eyes after cataract extraction with appropriate handling of perioperative inflammation.
Keywords: Cataract; inflammation; phacoemulsification; uveitis.
Copyright: © 2022 Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

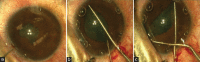
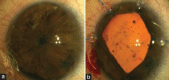
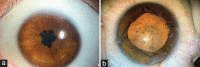
Comment in
-
Authors reply to letter to the editor.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023 Mar 9;37(1):78. doi: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_18_23. eCollection 2023 Jan-Mar. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36968770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Decision-making and management of uveitic cataract.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec;65(12):1329-1339. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_740_17. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29208813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraoperative intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection for prevention of postoperative inflammation and complications after phacoemulsification in patients with uveitic cataract.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun 4;21(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02017-y. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34088282 Free PMC article.
-
Sutureless combined 25-gauge vitrectomy, phacoemulsification, and posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation for management of uveitic cataract associated with posterior segment disease.Retina. 2008 Jul-Aug;28(7):941-6. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31816ed5c7. Retina. 2008. PMID: 18698295
-
Phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation in patients with uveitis.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2004 May;221(5):324-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-812851. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2004. PMID: 15162272
-
Controversies in intraocular lens implantation in pediatric uveitis.J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2016 Dec;6(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12348-016-0079-y. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2016. PMID: 27009616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Adjunctive Triamcinolone Acetonide in Post-traumatic Vitreoretinal Surgery: Current Insights and Future Perspectives.Cureus. 2024 Oct 7;16(10):e71040. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71040. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39525235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Authors reply to letter to the editor.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023 Mar 9;37(1):78. doi: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_18_23. eCollection 2023 Jan-Mar. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36968770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment of Behçet Uveitis in Türkiye.Turk J Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 28;54(4):198-204. doi: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2024.89346. Turk J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39205423 Free PMC article.
-
How Safe is Nd: YAG Laser Capsulotomy in Patients with Uveitis? Outcomes of a Long-Term Study.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 16;36(1):72-77. doi: 10.4103/joco.joco_221_23. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39553324 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery on the uveitic cataract: Rare obstacles.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb 16;37(1):76-77. doi: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_6_23. eCollection 2023 Jan-Mar. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36968776 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lobo AM, Papaliodis GN. Perioperative evaluation and management of cataract surgery in uveitis patients. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2010;50:129–37. - PubMed
-
- Mehta S, Linton MM, Kempen JH. Outcomes of cataract surgery in patients with uveitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;158:676–92.e7. - PubMed
-
- Dick AD, Tundia N, Sorg R, Zhao C, Chao J, Joshi A, et al. Risk of Ocular complications in patients with noninfectious intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, or panuveitis. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:655–62. - PubMed
-
- Jones NP. The Manchester uveitis clinic: The first 3000 patients, 2: Uveitis manifestations, complications, medical and surgical management. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2015;23:127–34. - PubMed
-
- AlBloushi AF, Alfawaz AM, Al-Dahmash SA, Al Owaifeer AM, AlEnezi SH, Al-Fakhri AS, et al. Incidence, risk factors and surgical outcomes of cataract among patients with uveitis in a university referral hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2019;27:1105–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
