Research on the optimization of financing scheme of long-term care insurance in China based on system dynamics simulation
- PMID: 36211654
- PMCID: PMC9538358
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.908864
Research on the optimization of financing scheme of long-term care insurance in China based on system dynamics simulation
Abstract
Objective: The aging population in China highlights the significance of long-term care insurance (LTCI). This study provides policy suggestions for China to establish a sustainable LTCI financing mechanism by predicting the trend of funds balance and screening the appropriate financing scheme.
Method: A system dynamics model (SDM) of LTCI funds was constructed by clarifying the current situation and its main influencing factors of revenue and expenditure of LTCI funds in China. Also, through literature research and expert consultation, we found the intervention goals and predicted the changing trend of LTCI fund balance from 2020 to 2050 under different intervention schemes.
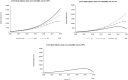
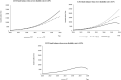
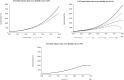
Results: The SDM of LTCI financing passes the dimensional consistency test, structural test, and historical test. Therefore, it can objectively reflect the structure and behavior of the financing system. It is found that the factors affecting the revenue and expenditure system of LTCI funds mainly include economic factors, demographic factors, and other factors. By adjusting three intervention indicators, namely, individual payment rate, reimbursement proportion, and severe disability rate, this study produces 45 financing combination schemes. By comparing the changing trend of LTCI fund balance under different intervention schemes, according to the screening principle, five better financing schemes are finally selected. These five financing schemes have no deficit and excessive balance in the forecast period, which is in line with the principle of sustainability. It can provide a reference for the selection of financing schemes in pilot areas.
Discussion: This study has optimized the policy of the LTCI financing mechanism, determined the suitable LTCI participants, financing channels and levels, and screened out the suitable LTCI financing policy optimization scheme for China. By appropriately increasing the individual payment rate, strengthening the disability intervention of the elderly, formulating scientific and objective disability evaluation standards, and finally establishing a dynamic financing adjustment mechanism of LTCI. This study can provide a basis for the scientific formulation of the LTCI financing mechanism in China and provide a reference for developing countries to establish a sustainable LTCI.
Keywords: financing mechanism; long-term care insurance; simulation and optimization; sustainability; system dynamic model.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Fu, Wang and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Life expectancy, long-term care demand and dynamic financing mechanism simulation: an empirical study of Zhejiang Pilot, China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Apr 15;24(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10875-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38622660 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Financing Mechanism of Long-Term Care Insurance in Xiamen, China: A System Dynamics Simulation.Front Public Health. 2021 Aug 16;9:714044. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.714044. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34485237 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Smart Healthcare in LTCI, Outpatient Mutual-Aid Guarantee Mechanism, and Sustainability of Medical Insurance Fund for Urban Employees.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Jan 7;2022:3406977. doi: 10.1155/2022/3406977. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35035822 Free PMC article.
-
Review of evolution of the public long-term care insurance (LTCI) system in different countries: influence and challenge.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Nov 20;20(1):1057. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05878-z. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 33218328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of long-term care insurance pilot city policies in China: a cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 21;13:1570794. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1570794. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40190763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research on the income and expenditure forecast of long-term care insurance fund in Shihezi City based on community care.Front Public Health. 2024 May 13;12:1329155. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1329155. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38803815 Free PMC article.
-
The financing sustainability of long-term care insurance: an example from Nanning, China.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 22;13:1454037. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1454037. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40331119 Free PMC article.
-
Life expectancy, long-term care demand and dynamic financing mechanism simulation: an empirical study of Zhejiang Pilot, China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Apr 15;24(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10875-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38622660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu X, Chen L. Projection of long-term care costs in China, 2020–2050: based on the Bayesian quantile regression method. Sustainability. (2019) 11:3530. 10.3390/su11133530 - DOI
-
- Main Data of the Seventh National Population Census. (2021). Available online at: http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202105/t20210510_1817185.html. (accessed 19 March, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

