A newly discovered PD-L1 B-cell epitope peptide vaccine (PDL1-Vaxx) exhibits potent immune responses and effective anti-tumor immunity in multiple syngeneic mice models and (synergizes) in combination with a dual HER-2 B-cell vaccine (B-Vaxx)
- PMID: 36211807
- PMCID: PMC9542669
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2127691
A newly discovered PD-L1 B-cell epitope peptide vaccine (PDL1-Vaxx) exhibits potent immune responses and effective anti-tumor immunity in multiple syngeneic mice models and (synergizes) in combination with a dual HER-2 B-cell vaccine (B-Vaxx)
Abstract
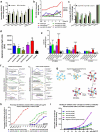
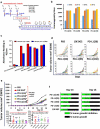
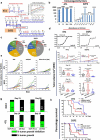
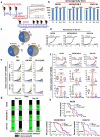
Blockade of checkpoint receptors with monoclonal antibodies against CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1 has shown great clinical success in several cancer subtypes, yielding unprecedented responses albeit a significant number of patients develop resistance and remain refractory. Both PD-1/PD-L1 and HER-2 signaling pathway inhibitors have limited efficacy and exhibits significant toxicities that limit their use. Ongoing clinical studies support the need for rationale combination of immuno-oncology agents to make a significant impact in the lives of cancer patients. We introduce the development of a novel chimeric PD-L1 B-cell peptide epitope vaccine (amino acid 130-147) linked to a "promiscuous" T cell measles virus fusion (MVF) peptide (MVF-PD-L1(130); PDL1-Vaxx) or linked to tetanus toxoid (TT3) TT3-PD-L1 (130) via a linker (GPSL). These vaccine constructs are highly immunogenic and antigenic in several syngeneic animal models. The PD-L1 vaccines elicited high titers of polyclonal antibodies that inhibit tumor growth in multiple syngeneic cancer models, eliciting antibodies of different subtypes IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3, induced PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, decreased proliferation, induced apoptosis and caused ADCC of tumor cells. The PDL1-Vaxx induces similar inhibition of tumor growth versus the standard anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody in both syngeneic BALB/c and C57BL/6J mouse models. The combination of PDL1-Vaxx with HER-2 vaccine B-Vaxx demonstrated synergistic tumor inhibition in D2F2/E2 carcinoma cell line. The anti-PDL1-Vaxx block PD-1/PD-L1 interaction and significantly prolonged anti-tumor responses in multiple syngeneic tumor models. The combination of HER-2 vaccine (B-Vaxx) with either PDL1-Vaxx or PD1-Vaxx demonstrated synergistic tumor inhibition. PDL1-Vaxx is a promising novel safe checkpoint inhibitor vaccine.
Keywords: B-cell epitope; CT26; D2F2/E2; PD-L1; Peptide-vaccine; immunotherapy.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Pravin T.P. Kaumaya is consultant to Imugene, Ltd. Nicholas Ede is CTO at Imugene. All the other authors declare no competing interests. Heather Darby is now at Assurance laboratories, Birmingham, AL. (hdarby@assurancelabs.com).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and antitumor efficacy of a novel human PD-1 B-cell vaccine (PD1-Vaxx) and combination immunotherapy with dual trastuzumab/pertuzumab-like HER-2 B-cell epitope vaccines (B-Vaxx) in a syngeneic mouse model.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Oct 1;9(1):1818437. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1818437. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 33117602 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Fluorescent Bead-Based Dual-Reporter Flow Analysis of PDL1-Vaxx Peptide Vaccine-Induced Antibody Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction.J Vis Exp. 2023 Jul 7;(197). doi: 10.3791/65467. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37486131
-
Novel chimeric CTLA-4 B-cell epitope peptide vaccines demonstrate effective anti-tumor immunity with/without PD1/PDL1 blockade in multiple syngeneic murine models of breast and colorectal cancers.Mol Cancer Ther. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-24-0908. Online ahead of print. Mol Cancer Ther. 2025. PMID: 40325996
-
B-cell epitope peptide cancer vaccines: a new paradigm for combination immunotherapies with novel checkpoint peptide vaccine.Future Oncol. 2020 Aug;16(23):1767-1791. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0224. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Future Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32564612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the vaccine potential of an in silico designed FepA peptide vaccine against Shigella flexneri in mice model.Vaccine X. 2024 May 8;18:100493. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100493. eCollection 2024 Jun. Vaccine X. 2024. PMID: 38812954 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Exon 3 Is a Hidden Switch of Its Expression and Function in Oral Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 3;24(9):8193. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098193. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175900 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic and predictive roles of plasma C-reactive protein and PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Aug;12(15):16087-16097. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6262. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37329173 Free PMC article.
-
Inappropriate Expression of PD-1 and CTLA-4 Checkpoints in Myeloma Patients Is More Pronounced at Diagnosis: Implications for Time to Progression and Response to Therapeutic Checkpoint Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5730. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065730. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982802 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Clinical, Molecular and Immunological Characterization of Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinomas Reveals an Immune Escape Mechanism That May Influence Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 23;24(13):10558. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310558. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445733 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
