Mapping intellectual structures and research hotspots in the application of artificial intelligence in cancer: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36212413
- PMCID: PMC9535738
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955668
Mapping intellectual structures and research hotspots in the application of artificial intelligence in cancer: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI) is more and more widely used in cancer, which is of great help to doctors in diagnosis and treatment. This study aims to summarize the current research hotspots in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Cancer (AAIC) and to assess the research trends in AAIC.
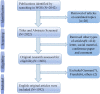
Methods: Scientific publications for AAIC-related research from 1 January 1998 to 1 July 2022 were obtained from the Web of Science database. The metrics analyses using bibliometrics software included publication, keyword, author, journal, institution, and country. In addition, the blustering analysis on the binary matrix was performed on hot keywords.
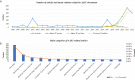
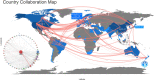
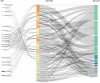
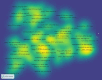
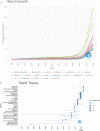
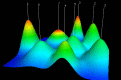
Results: The total number of papers in this study is 1592. The last decade of AAIC research has been divided into a slow development phase (2013-2018) and a rapid development phase (2019-2022). An international collaboration centered in the USA is dedicated to the development and application of AAIC. Li J is the most prolific writer in AAIC. Through clustering analysis and high-frequency keyword research, it has been shown that AI plays a significantly important role in the prediction, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of cancer. Classification, diagnosis, carcinogenesis, risk, and validation are developing topics. Eight hotspot fields of AAIC were also identified.
Conclusion: AAIC can benefit cancer patients in diagnosing cancer, assessing the effectiveness of treatment, making a decision, predicting prognosis and saving costs. Future AAIC research may be dedicated to optimizing AI calculation tools, improving accuracy, and promoting AI.
Keywords: ai; application; bibliometric analysis; cancer; research hotspots.
Copyright © 2022 Lyu, Wang, Meng, Fan, Ma, Xiao, Cao, Lin and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Research hotspots and trends of artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric and visualized study.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Nov 10;20(12):20405-20421. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023902. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 38124558
-
Visualizing knowledge evolution trends and research hotspots of artificial intelligence in colorectal cancer: A bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 28;12:925924. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925924. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36518311 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer: a bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 2;12:973999. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.973999. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35982967 Free PMC article.
-
International publication trends in the application of artificial intelligence in ophthalmology research: an updated bibliometric analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Mar 15;11(5):219. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3773. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37007552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research on artificial intelligence, machine and deep learning in medicine: global characteristics, readiness, and equity.Global Health. 2025 Jun 8;21(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12992-025-01128-1. Global Health. 2025. PMID: 40484942 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

