Elevated plasma EDA fibronectin in primary myelofibrosis is determined by high allele burden of JAK2 V617F mutation and strongly predicts splenomegaly progression
- PMID: 36212480
- PMCID: PMC9532599
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.987643
Elevated plasma EDA fibronectin in primary myelofibrosis is determined by high allele burden of JAK2 V617F mutation and strongly predicts splenomegaly progression
Abstract
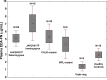
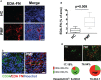
In primary myelofibrosis, extra-domain A fibronectin (EDA-FN), the result of alternative splicing of FN gene, sustains megakaryocyte proliferation and confers a pro-inflammatory phenotype to bone marrow cell niches. In this work we assessed the levels of circulating EDA-FN in plasma samples of 122 patients with primary myelofibrosis. Patients with a homozygous JAK2V617F genotype displayed the higher level of plasma EDA-FN. Increased EDA-FN levels were associated with anemia, elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, bone marrow fibrosis and splanchnic vein thrombosis at diagnosis. While no correlation was observed with CD34+ hematopoietic stem cell mobilization, elevated blood level of EDA-FN at diagnosis was a predictor of large splenomegaly (over 10 cm from the left costal margin) outcome. Thus, EDA-FN expression in primary myelofibrosis may represent the first marker of disease progression, and a novel target to treat splenomegaly.
Keywords: extra domain A; fibronectin; neoangiogenesis; primary myelofibrosis; splenomegaly.
Copyright © 2022 Malara, Gruppi, Massa, Tira, Rosti, Balduini and Barosi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer SM declared a past co-authorship with one of the authors AB to the handling Editor.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

