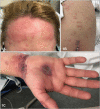
No abstract available
Keywords:
LABD, linear IgA bullous dermatosis; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; Sweet; Sweet syndrome; Sweet’s; acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis; celecoxib; celecoxib-induced; drug-induced; itch; itchy; pruritic; pruritus.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
-
Walker D.C., Cohen P.R. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-associated acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis: case report and review of drug-induced Sweet's syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34(5 Pt 2):918–923. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90080-8.
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Rochet N.M., Chavan R.N., Cappel M.A., Wada D.A., Gibson L.E. Sweet syndrome: clinical presentation, associations, and response to treatment in 77 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(4):557–564. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.023.
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Fye K.H., Crowley E., Berger T.G., LeBoit P.E., Connolly M.K. Celecoxib-induced Sweet's syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45(2):300–302. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.114587.
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Oh E.H., Shin J.M., Hong J.H., Kim J.S., Ro Y.S., Ko J.Y. Drug-induced bullous Sweet's syndrome by celecoxib. J Dermatol. 2016;43(9):1092–1093. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13337.
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Rosmaninho A., Lobo I., Selores M. Sweet's syndrome associated with the intake of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2011;30(4):298–301. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2011.579929.
-
DOI
-
PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous