Lignocellulose dissociation with biological pretreatment towards the biochemical platform: A review
- PMID: 36212906
- PMCID: PMC9535326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100445
Lignocellulose dissociation with biological pretreatment towards the biochemical platform: A review
Abstract
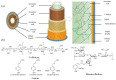
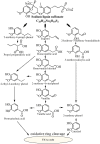
Lignocellulose utilization has been gaining great attention worldwide due to its abundance, accessibility, renewability and recyclability. Destruction and dissociation of the cross-linked, hierarchical structure within cellulose hemicellulose and lignin is the key procedure during chemical utilization of lignocellulose. Of the pretreatments, biological treatment, which can effectively target the complex structures, is attractive due to its mild reaction conditions and environmentally friendly characteristics. Herein, we report a comprehensive review of the current biological pretreatments for lignocellulose dissociation and their corresponding degradation mechanisms. Firstly, we analyze the layered, hierarchical structure of cell wall, and the cross-linked network between cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, then highlight that the cracking of β-aryl ether is considered the key to lignin degradation because of its dominant position. Secondly, we explore the effect of biological pretreatments, such as fungi, bacteria, microbial consortium, and enzymes, on substrate structure and degradation efficiency. Additionally, combining biological pretreatment with other methods (chemical methods and catalytic materials) may reduce the time necessary for the whole process, which also help to strengthen the lignocellulose dissociation efficiency. Thirdly, we summarize the related applications of lignocellulose, such as fuel production, chemicals platform, and bio-pulping, which could effectively alleviate the energy pressure through bioconversion into high value-added products. Based on reviewing of current progress of lignocellulose pretreatment, the challenges and future prospects are emphasized. Genetic engineering and other technologies to modify strains or enzymes for improved biotransformation efficiency will be the focus of future research.
Keywords: Biochemical platform; Biological pretreatment; Cross-linked structure; Lignin barrier; Lignocellulose.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Lignocellulose biomass bioconversion during composting: Mechanism of action of lignocellulase, pretreatment methods and future perspectives.Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;286(Pt 1):131635. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131635. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34346339 Review.
-
Engineering Ligninolytic Consortium for Bioconversion of Lignocelluloses to Ethanol and Chemicals.Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(2):108-119. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666180122105835. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 29359652 Review.
-
Development of different pretreatments and related technologies for efficient biomass conversion of lignocellulose.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Mar 31;202:256-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.036. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35032493 Review.
-
Hydrolysis of lignocellulose to succinic acid: a review of treatment methods and succinic acid applications.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023 Jan 2;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13068-022-02244-5. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023. PMID: 36593503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unconventional Pretreatment of Lignocellulose with Low-Temperature Plasma.ChemSusChem. 2017 Jan 10;10(1):14-31. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201601381. Epub 2016 Dec 27. ChemSusChem. 2017. PMID: 27922209 Review.
Cited by
-
Straw from Different Crop Species Recruits Different Communities of Lignocellulose-Degrading Microorganisms in Black Soil.Microorganisms. 2024 May 5;12(5):938. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050938. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792768 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the pretreatment and hydrolysis of a mixture of coffee husk, cowpea bean husk and cocoa pod for bacterial cellulose production.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025 Jun;48(6):993-1006. doi: 10.1007/s00449-025-03158-w. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025. PMID: 40183858 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Formation of Lignin Particles Through Melt-Extrusion for Active Biodegradable Food Packaging.ACS Omega. 2024 May 29;9(23):24346-24355. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10113. eCollection 2024 Jun 11. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38882124 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring carbohydrate extraction from biomass using deep eutectic solvents: Factors and mechanisms.iScience. 2023 Aug 19;26(9):107671. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107671. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37680471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial communities and their role in enhancing hemp fiber quality through field retting.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 5;108(1):501. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13323-y. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39500773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baruah J., Nath B.K., Sharma R., Kumar S., Deka R.C., Baruah D.C., Kalita E. Recent trends in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for value-added products. Front. Energy Res. 2018;6:141. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2018.00141. - DOI
-
- Shirkavand E., Baroutian S., Gapes D.J., Young B.R. Combination of fungal and physicochemical processes for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment – a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016;54:217–234. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

