Scientific authorship by gender: trends before and during a global pandemic
- PMID: 36212912
- PMCID: PMC9529602
- DOI: 10.1057/s41599-022-01365-4
Scientific authorship by gender: trends before and during a global pandemic
Abstract
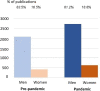
Many fields of science are still dominated by men. COVID-19 has dramatically changed the nature of work, including for scientists, such as lack of access to key resources and transition to online teaching. Further, scientists face the pandemic-related stressors common to other professions (e.g., childcare, eldercare). As many of these activities fall more heavily on women, the pandemic may have exacerbated gender disparities in science. We analyzed self-identified gender of corresponding author for 119,592 manuscripts from 151 countries submitted January 2019 to July 2021 to the Institute of Physics (IOP) portfolio of 57 academic journals, with disciplines of astronomy and astrophysics, bioscience, environmental science, materials, mathematics, physics, and interdisciplinary research. We consider differences by country, journal, and pre-pandemic versus pandemic periods. Gender was self-identified by corresponding author for 82.9% of manuscripts (N = 99,114 for subset of submissions with gender). Of these manuscripts, authors were 82.1% male, 17.8% female, and 0.08% non-binary. Most authors were male for all countries (country-specific values: range 0.0-100.0%, median 86.1%) and every journal (journal-specific values range 63.7-91.5%, median 83.7%). The contribution of female authors was slightly higher in the pandemic (18.7%) compared to pre-pandemic (16.5%). However, prior to the pandemic, the percent of submissions from women had been increasing, and this value slowed during the pandemic. Contrary to our hypothesis, we did not find that manuscript submissions from women decreased during the pandemic, although the rate of increased submissions evident prior to the pandemic slowed. In both pre-pandemic and pandemic periods, authorship was overwhelmingly male for all journals, countries, and fields. Further research is needed on impacts of the pandemic on other measures of scientific productivity (e.g., accepted manuscripts, teaching), scientific position (e.g., junior vs. senior scholars), as well as the underlying gender imbalance that persisted before and during the pandemic.
Keywords: Education; Science, technology and society.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Was the COVID-19 Pandemic Associated with Gender Disparities in Authorship of Manuscripts Submitted to Clinical Neuropsychology Journals?J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2023 Jan;29(1):105-109. doi: 10.1017/S1355617721001375. Epub 2021 Dec 9. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2023. PMID: 34879885
-
Female authorship of covid-19 research in manuscripts submitted to 11 biomedical journals: cross sectional study.BMJ. 2021 Oct 6;375:n2288. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n2288. BMJ. 2021. PMID: 34615650 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Author Sex and Manuscript Acceptance Rates among Pulmonary and Critical Care Journals.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023 Feb;20(2):215-225. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202203-277OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023. PMID: 35588358 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Disparities in Academic Radiology Authorship: A 13-Year Review.Acad Radiol. 2023 Aug;30(8):1714-1720. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.10.031. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Acad Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36424312 Review.
-
Neuro-oncology authorship trends in gender since 1944: a systematic review of 14,020 articles from five top-tier academic journals.J Neurosurg. 2022 Nov 25;139(1):1-10. doi: 10.3171/2022.10.JNS221183. Print 2023 Jul 1. J Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 36433875
Cited by
-
Nature publishes too few papers from women researchers - that must change.Nature. 2024 Mar;627(8002):7-8. doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-00640-5. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38448701 No abstract available.
-
Representation of women in scientific subjects: overview of systematic reviews investigating career progress in academic publishing with a focus on mental health.BJPsych Open. 2025 Mar 12;11(2):e49. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2024.820. BJPsych Open. 2025. PMID: 40071959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gender parity in high impact neurology journals.eNeurologicalSci. 2023 Aug 23;33:100476. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2023.100476. eCollection 2023 Dec. eNeurologicalSci. 2023. PMID: 37691968 Free PMC article.
-
The Issue of Gender Bias Represented in Authorship in the Fields of Exercise and Rehabilitation: A 5-Year Research in Indexed Journals.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2023 Jan 30;8(1):18. doi: 10.3390/jfmk8010018. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2023. PMID: 36810502 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring gender from first names: Comparing the accuracy of Genderize, Gender API, and the gender R package on authors of diverse nationality.PLOS Digit Health. 2024 Oct 29;3(10):e0000456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000456. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLOS Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39471154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adekola O, Namawejje H, Oguguah N et al. (2022) How COVID-19 has affected research productivity in Africa: lessons for the future. Afr Geogr Rev. 10.1080/19376812.2022.2063142
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials