fMRI studies evaluating central respiratory control in humans
- PMID: 36213203
- PMCID: PMC9537466
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2022.982963
fMRI studies evaluating central respiratory control in humans
Erratum in
-
Erratum: fMRI studies evaluating central respiratory control in humans.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Mar 13;17:1176605. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1176605. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 36994238 Free PMC article.
Abstract
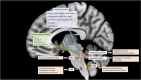
A plethora of neural centers in the central nervous system control the fundamental respiratory pattern. This control is ensured by neurons that act as pacemakers, modulating activity through chemical control driven by changes in the O2/CO2 balance. Most of the respiratory neural centers are located in the brainstem, but difficult to localize on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) due to their small size, lack of visually-detectable borders with neighboring areas, and significant physiological noise hampering detection of its activity with functional MRI (fMRI). Yet, several approaches make it possible to study the normal response to different abnormal stimuli or conditions such as CO2 inhalation, induced hypercapnia, volitional apnea, induced hypoxia etc. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the majority of available studies on central respiratory control in humans.
Keywords: brainstem; breathing; central respiratory control; fMRI; forebrain.
Copyright © 2022 Ciumas, Rheims and Ryvlin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allen L. A., Harper R. M., Kumar R., Guye M., Ogren J. A., Lhatoo S. D., et al. . (2017). Dysfunctional brain networking among autonomic regulatory structures in temporal lobe epilepsy patients at high risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 8:544. 10.3389/fneur.2017.00544 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

