Involvement of Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Kinase (ROCK) in BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cardiovascular Toxicity
- PMID: 36213346
- PMCID: PMC9537085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.06.004
Involvement of Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Kinase (ROCK) in BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cardiovascular Toxicity
Abstract
Background: Second- and third-generation BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are associated with cardiovascular adverse events (CVAEs) in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) leukemia.
Objectives: We hypothesized that second- and third-generation BCR-ABL1 TKIs may cause CVAEs through the activation of Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinase (ROCK).
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 53 Ph+ patients on TKIs and 15 control patients without Ph+ leukemia were assessed for ROCK activity through capillary electrophoresis (median follow-up = 26 months [Q1-Q3: 5-37 months]). We also investigated the effects of TKIs and ROCK on endothelial dysfunction in vitro, which could contribute to CVAEs.
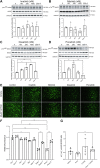
Results: Patients receiving second- and third-generation TKIs had 1.6-fold greater ROCK activity compared with patients receiving imatinib and control patients. Elevated ROCK activity was associated with an increased incidence of CVAEs in Ph+ leukemia patients. In endothelial cells in vitro, we found that dasatinib and ponatinib treatment led to changes in actin intensity and endothelial permeability, which can be reversed by pharmacologic inhibition of ROCK. Ponatinib led to decreased cell proliferation, but this was not accompanied by senescence. Dasatinib and ponatinib treatment led to phosphor-inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and decreased nitric oxide production. ROCK inhibition reversed endothelial permeability and endothelial nitric oxide synthase-related endothelial dysfunction. Imatinib and nilotinib induce phosphorylation of p190RhoGAP.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest ROCK activity may be a prognostic indicator of CVAEs in patients receiving BCR-ABL1 TKIs. With further study, ROCK inhibition may be a promising approach to reduce the incidence of CVAEs associated with second- and third-generation BCR-ABL1 TKIs.
Keywords: 2G/3G, second/third generation; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CVAE, cardiovascular adverse event; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; Ph+, Philadelphia chromosome-positive; Philadelphia chromosome; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinase; Rho-associated protein kinase; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; chronic myeloid leukemia; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; endothelial dysfunction; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a Stanford Medical Scholars Fellowship and AHA Predoctoral Fellowship to Dr Yu; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute T32-HL007381 to Dr Sladojevic; grant support from Ariad to Dr Larson; and National Institutes of Health R01-HL136962 to Dr Liao. Dr Larson reports being a consultant or advisor to Amgen, Ariad/Takeda, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, CVS/Caremark, Epizyme, MorphoSys, and Novartis; has received clinical research support to his institution from Astellas, Celgene, Cellectis, Daiichi Sankyo, Forty-Seven/Gilead, Novartis, and Rafael Pharmaceuticals; and has received royalties from UpToDate. Dr Liao reports being a consultant or advisor to Esperion. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures






References
-
- Douxfils J., Haguet H., Mullier F., Chatelain C., Graux C., Dogné J.-M. Association between BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors for chronic myeloid leukemia and cardiovascular events, major molecular response, and overall survival: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:625–632. - PubMed
-
- Giles F.J., Mauro M.J., Hong F., et al. Rates of peripheral arterial occlusive disease in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase treated with imatinib, nilotinib, or non-tyrosine kinase therapy: a retrospective cohort analysis. Leukemia. 2013;27:1310–1315. - PubMed
-
- Lipton J.H., Chuah C., Guerci-Bresler A., et al. Ponatinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukaemia: an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:612–621. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

