The Beneficial Effects of Geniposide on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Review
- PMID: 36213380
- PMCID: PMC9532263
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S378976
The Beneficial Effects of Geniposide on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Review
Abstract
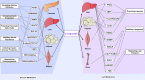
Geniposide is a naturally sourced active ingredient that has diverse pharmacological effects and great potential in improving or treating different kinds of diseases. In recent years, more and more studies have confirmed that geniposide can improve glucose and lipid metabolism disorder, which is an increasingly prevalent health problem causing various metabolic diseases globally. Our review aims to summarize basic information on the pharmacological effects of geniposide on glucolipid metabolism. Geniposide increases glucose utilization and insulin production, protects pancreatic islet β cells, inhibits insulin resistance and hepatic glucose production, and suppresses gluconeogenesis. While in the aspect of lipid metabolism, geniposide can promote lipolysis, inhibit lipogenesis, and regulate lipid transport. Geniposide ameliorates lipid and glucose metabolic disorders, improving the entire glycolipid metabolism network in a three-dimensional manner at the level of molecular mechanism. Growing evidence revealed that geniposide may serve as an effective drug to combat metabolic diseases for the time to come.
Keywords: Gardenia Jasminoides Ellis; geniposide; glucolipid metabolism; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; metabolic disease; naturally sourced active ingredient; pharmacological evidence.
© 2022 Gao and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Hasebe T, Hasebe N. Impact of risk factors related to metabolic syndrome on acute myocardial infarction in younger patients. Hypertens Res. 2022;45:287–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

