Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- PMID: 36213382
- PMCID: PMC9490861
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2022-0474
Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
Abstract
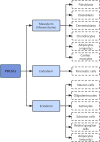
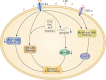
Periodontitis is a common disease that is difficult to treat, and if not controlled in time, it causes severe conditions, such as alveolar bone resorption and tooth loosening and loss. Periodontal ligament stem cells constitute a promising cell source for regenerative treatment of periodontitis due to their high osteogenic differentiation capacity. PDLSC osteogenesis plays a central role in periodontal regeneration through successive cytokine-mediated signaling pathways and various biochemical and physicochemical factors. However, this process is inhibited in the inflammatory periodontitis environment due to high concentrations of lipopolysaccharide. Here, we review the mechanisms that influence the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal stem cells in this inflammatory microenvironment.
Keywords: inflammatory environment; lipopolysaccharide; osteogenic differentiation; periodontal membrane stem cells.
© 2022 Shenghao Jin et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
