Immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant among school-aged children with 2-dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines followed by BNT162b2 booster
- PMID: 36213592
- PMCID: PMC9531410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2022.100221
Immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant among school-aged children with 2-dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines followed by BNT162b2 booster
Abstract
Background: A primary series of 2-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccines based on an ancestral strain generate inadequate neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. This study aimed to describe the immune response from giving healthy school-aged children who previously received 2 inactivated vaccines an mRNA BNT162b2 booster.
Methods: Healthy children aged 5-11 years who received 2 doses of CoronaVac or Covilo were enrolled and received 10 µg BNT162b2 intramuscularly. Neutralizing antibody against Omicron variant was measured at pre-booster and 14-21 days post-booster by surrogate virus neutralization test (sVNT, %inhibition) and pseudovirus neutralization test (pVNT, ID50). Antibody responses were compared with a parallel cohort of children who received 2 doses of BNT162b2 3 weeks apart.
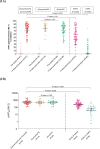
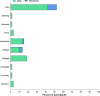
Results: From April to May 2022, 59 children with a mean age (SD) of 8.5 years (1.7) were enrolled: 20 CoronaVac and 39 Covilo recipients. The median interval from the primary series was 49 days (IQR 33-51). After booster, the geometric means (GMs) of sVNT and pVNT were 72.2 %inhibition (95 %CI 67.2-77.6) and 499 (95 %CI 399-624), respectively. The proportion of children with sVNT against Omicron strain ≥68 %inhibition increased from none to 70.2 %. The geometric mean ratio (GMR) of sVNT and pVNT compared with a parallel cohort were 4.3 and 12.2, respectively. The GMR of sVNT and pVNT between children who received booster dose at >6-week interval were 1.2 (95 %CI 1.1-1.3). and 1.8 (95 %CI 1.2-2.7) compared with 4-6 weeks interval.
Conclusion: A regimen of 2-dose of inactivated vaccine followed by BNT162b2 booster dose elicited high neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variants in healthy school-aged children.
Keywords: BNT162b2; Booster vaccination; Inactivated COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2 antibody; School-aged children.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Health Emergency Dashboard. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. <https://covid19.who.int/> [accessed on 30 May 2022].
-
- US FDA. FDA Authorizes Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine for Emergency Use in Children 5 through 11 Years of Age; October 29, 2021. <https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-authorizes-pfize... [accessed on 5 May 2022].
-
- European Medicines Agency. EMA recommends approval of Spikevax for children aged 6 to 11. <https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-approval-spikevax-child... [accessed on 5 May 2022].
-
- Bridge Consulting. China COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker. <https://bridgebeijing.com/our-publications/our-publications-1/china-covi... [accessed on 5 May 2022].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

