Mesenchymal stem cell therapy on top of triple therapy with remdesivir, dexamethasone, and tocilizumab improves PaO2/FiO2 in severe COVID-19 pneumonia
- PMID: 36213639
- PMCID: PMC9537613
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1001979
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy on top of triple therapy with remdesivir, dexamethasone, and tocilizumab improves PaO2/FiO2 in severe COVID-19 pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Despite patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) receiving standard triple therapy, including steroids, antiviral agents, and anticytokine therapy, health condition of certain patients continue to deteriorate. In Taiwan, the COVID-19 mortality has been high since the emergence of previous variants of this disease (such as alpha, beta, or delta). We aimed to evaluate whether adjunctive infusion of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (hUC-MSCs) on top of dexamethasone, remdesivir, and tocilizumab improves pulmonary oxygenation and suppresses inflammatory cytokines in patients with severe COVID-19.
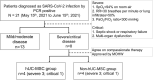
Methods: Hospitalized patients with severe or critical COVID-19 pneumonia under standard triple therapy were separated into adjuvant hUC-MSC and non-hUC-MSC groups to compare the changes in the arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)/fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) ratio and biological variables.
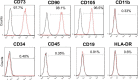
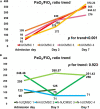
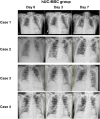
Results: Four out of eight patients with severe or critical COVID-19 received either one (n = 2) or two (n = 2) doses of intravenous infusions of hUC-MSCs using a uniform cell dose of 1.0 × 108. Both high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level and monocyte distribution width (MDW) were significantly reduced, with a reduction in the levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-13, IL-12p70 and vascular endothelial growth factor following hUC-MSC transplantation. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio increased from 83.68 (64.34-126.75) to 227.50 (185.25-237.50) and then 349.56 (293.03-367.92) within 7 days after hUC-MSC infusion (P < 0.001), while the change of PaO2/FiO2 ratio was insignificant in non-hUC-MSC patients (admission day: 165.00 [102.50-237.61]; day 3: 100.00 [72.00-232.68]; day 7: 250.00 [71.00-251.43], P = 0.923).
Conclusion: Transplantation of hUC-MSCs as adjunctive therapy improves pulmonary oxygenation in patients with severe or critical COVID-19. The beneficial effects of hUC-MSCs were presumably mediated by the mitigation of inflammatory cytokines, characterized by the reduction in both hs-CRP and MDW.
Keywords: COVID-19; arterial partial pressure of oxygen vs. fraction of inspired oxygen; human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; inflammatory cytokines; monocyte distribution width.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Chang, Lin, Ho, Cheng, Shih, Chou, Lin, Chi, Lu, Tien, Wu, Chang, Hsu, Shyu, Cho and Jeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Double-blind, randomized, controlled, trial to assess the efficacy of allogenic mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19 (COVID-AT): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 6;22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04964-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33407777 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of severe COVID-19 with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Aug 18;11(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01875-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32811531 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: A 3-Month Follow-Up Study Following Hospital Discharge.Stem Cells Dev. 2021 Aug 1;30(15):773-781. doi: 10.1089/scd.2021.0015. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Stem Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 34044609
-
What is the impact of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on clinical treatment?Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Dec 1;11(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02011-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33261658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of RCTs Pooling Evidence on Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapeutic Applications During COVID-19 Epidemic: A Systematic Review.Biologics. 2023 May 18;17:85-112. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S404421. eCollection 2023. Biologics. 2023. PMID: 37223116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. WHO (2020) Coronavirus Disease (Covid-10) Pandemic. Geneva: WHO; (2021).
-
- NIH. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Bethesda, MD: NIH; (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

