Risk Predictive Model Based on Three DDR-Related Genes for Predicting Prognosis, Therapeutic Sensitivity, and Tumor Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36213834
- PMCID: PMC9546689
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4869732
Risk Predictive Model Based on Three DDR-Related Genes for Predicting Prognosis, Therapeutic Sensitivity, and Tumor Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
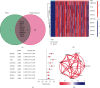
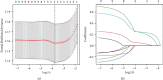
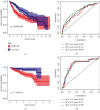
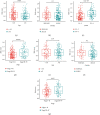
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the seventh most common malignancy and the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths. Tumor mutational load, genomic instability, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were associated with DNA damage response and repair gene changes. The goal of this study is to estimate the chances of patients with HCC surviving their disease by constructing a DNA damage repair- (DDR-) related gene profile. The International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) provided us with the mRNA expression matrix as well as clinical information relevant to HCC patients. Using Cox regression and LASSO analysis, DEGs strongly related to general survival were discovered in the differentially expressed gene (DEG) study. In order to assess the model's accuracy, Kaplan-Meier (KM) and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) were used. In order to compute the immune cell infiltration score and immune associated pathway activity, a single-sample gene set enrichment analysis was performed. A three-gene signature (CDC20, TTK, and CENPA) was created using stability selection and LASSO COX regression. In comparison to the low-risk group, the prognosis for the high-risk group was surprisingly poor. In the ICGC datasets, the predictive characteristic was confirmed. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was calculated for each cohort. The risk mark for HCC patients is a reliable predictor according to multivariate Cox regression analysis. According to ssGSEA, this signature was highly correlated with the immunological state of HCC patients. There was a significant correlation between the expression levels of prognostic genes and cancer cells' susceptibility to antitumor therapies. Overall, a distinct gene profile associated with DDR was identified, and this pattern may be able to predict HCC patients' long-term survival, immune milieu, and chemotherapeutic response.
Copyright © 2022 Renzhi Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and Validation of a Novel Six-Gene Expression Signature for Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:723271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723271. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925311 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a 25-lncRNA prognostic signature for early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 30;21(1):1165. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08827-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34717566 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a DNA Damage Response and Repair-Related Gene-Pair Signature for Prognosis Stratification Analysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 5;13:857060. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857060. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496321 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of an autophagy-related prognostic model for predicting survival based on TCGA and ICGC database in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(6):3154-3168. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1130. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36636069 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Liver Progenitor Cell-Related Genes Signature Predicting Overall Survival for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211041425. doi: 10.1177/15330338211041425. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34866477 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

