Interventions and strategies to improve social support for caregivers of children with chronic diseases: An umbrella review
- PMID: 36213907
- PMCID: PMC9537372
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.973012
Interventions and strategies to improve social support for caregivers of children with chronic diseases: An umbrella review
Abstract
Background: Social support is an important approach to improve the psychosocial health status and promote positive coping for caregivers of children with chronic diseases. Such an approach can reduce parenting stress, help resolve parenting difficulties through the use of various social support relationships.
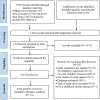
Methods: We performed an umbrella review methodology using the method of examination, analysis and synthesis of systematic reviews. A PRISMA flow diagram was used to show the search process. The Joanna Briggs Institute was used to appraise the quality of papers and a narrative synthesis was undertaken. Relevant English and Chinese systematic reviews were searched in Embase, PubMed, Web of science, OVID, CNKI, CBM, Wan Fang and Cochrane Library databases, until November 2021, June 2022.
Results: Out of 1,905 records, we included fourteen systematic reviews for a synthesis. Evidence to promote social support for caregivers of children with chronic diseases was identified from four key aspects: (i) Intervention content; (ii) Intervention forms; (iii) Intervention time; and (iv) Sources of support.
Conclusions: The findings of this review suggest that a combination of differing interventions, especially for early family, including the content of parenting training or education, attitude building and resource provision, which can implement online is recommend. More interventional studies and quantitative evidence syntheses are still needed.
Impact: Adequate social support is essential to promote the psychological wellbeing of caregivers of children with chronic diseases. In the early stage of children's diseases, integrating different content and forms of interventions for caregivers' families and actively helping caregivers to identify available support resources can improve social support. The findings from this review can be used to guide caregivers of children with chronic diseases and provide evidence for healthcare professionals and social workers to carry out relevant interventions.
Keywords: caregivers; children; chronic diseases; social support; umbrella review.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Lin, Gao, Wang and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interventions to address parenting stress among caregivers of children with chronic diseases: An umbrella review.J Clin Nurs. 2024 May;33(5):1626-1646. doi: 10.1111/jocn.17060. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Clin Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38323676
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
-
The experiences of caregivers of children with epilepsy: A meta-synthesis of qualitative research studies.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Sep 13;13:987892. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.987892. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36177220 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of family-centered care interventions on well-being of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review.F1000Res. 2024 May 29;12:790. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.133314.2. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38911944 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Stress and Coping in Caregivers of Children with Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: A Mixed-Method Study.Children (Basel). 2024 Aug 17;11(8):1008. doi: 10.3390/children11081008. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201942 Free PMC article.
-
Patient navigator programmes for children and adolescents with chronic diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 9;10(10):CD014688. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014688.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39382077
-
The roles of self-compassion and social support on the maternal adjustment to a child's hip dysplasia.J Health Psychol. 2025 Aug;30(9):2172-2182. doi: 10.1177/13591053241295892. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39569613 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of Caregivers on Access to Health Care for Children with CKD.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Sep 2;9(11):3177-3189. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.08.029. eCollection 2024 Nov. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39534191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan Y, Zhang L. “Family-centered” health management for children with chronic diseases. Jiangsu Health Serv Manag. (2013) 24:277–8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources