The Small RNA Teg41 Is a Pleiotropic Regulator of Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 36214557
- PMCID: PMC9670889
- DOI: 10.1128/iai.00236-22
The Small RNA Teg41 Is a Pleiotropic Regulator of Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
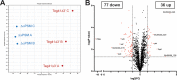
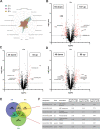
Previously, our group demonstrated a role for the small RNA (sRNA) Teg41 in regulating production of the alpha phenol-soluble modulin toxins (αPSMs) in Staphylococcus aureus. Overexpressing Teg41 increased αPSM production while deleting the 3' end of Teg41 (Teg41Δ3' strain) resulted in a decrease in αPSM production, reduced hemolytic activity of S. aureus culture supernatants, and attenuated virulence in a murine abscess model of infection. In this study, we further explore the attenuation of virulence in the Teg41Δ3' strain. Using both localized and systemic models of infection, we demonstrate that the Teg41Δ3' strain is more severely attenuated than an ΔαPSM mutant, strongly suggesting that Teg41 influences more than the αPSMs. Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of the wild-type and Teg41Δ3' strains reveals widespread alterations in transcript abundance and protein production in the absence of Teg41, confirming that Teg41 has pleiotropic effects in the cell. We go on to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying Teg41-mediated gene regulation. Surprisingly, results demonstrate that certain Teg41 target genes, including the αPSMs and βPSMs, are transcriptionally altered in the Teg41Δ3' strain, while other targets, specifically spa (encoding surface protein A), are regulated at the level of transcript stability. Collectively, these data demonstrate that Teg41 is a pleiotropic RNA regulator in S. aureus that influences expression of a variety of genes using multiple different mechanisms.
Keywords: AgrA; MgrA; PSM; Staphylococcus aureus; Teg41; protein A; regulation; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Small RNA Teg41 Regulates Expression of the Alpha Phenol-Soluble Modulins and Is Required for Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2019 Feb 5;10(1):e02484-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02484-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30723124 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus Global Regulator MgrA Modulates Clumping and Virulence by Controlling Surface Protein Expression.PLoS Pathog. 2016 May 4;12(5):e1005604. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005604. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27144398 Free PMC article.
-
MgrA Governs Adherence, Host Cell Interaction, and Virulence in a Murine Model of Bacteremia Due to Staphylococcus aureus.J Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 9;220(6):1019-1028. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz219. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31177268 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Regulation of Alpha-Toxin and the Phenol-Soluble Modulins by Peptidyl-Prolyl cis/trans Isomerase Enzymes in Staphylococcus aureus.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jun 16;11(6):343. doi: 10.3390/toxins11060343. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31208155 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus: the need for in vivo analysis of virulence factor regulation.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004 Oct 1;42(2):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2004.05.005. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15364098 Review.
Cited by
-
YjbH contributes to Staphylococcus aureus skin pathology and immune response through Agr-mediated α-toxin regulation.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2399798. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2399798. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39229975 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comparative Genomic Study Against Non-AML Isolates.Pathogens. 2025 Jun 24;14(7):627. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14070627. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40732675 Free PMC article.
-
SSR42 is a novel regulator of cytolytic activity in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2025 Jun 11;16(6):e0077225. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00772-25. Epub 2025 May 9. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40340377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morrison JM, Miller EW, Benson MA, Alonzo F, Yoong P, Torres VJ, Hinrichs SH, Dunman PM. 2012. Characterization of SSR42, a novel virulence factor regulatory RNA that contributes to the pathogenesis of a Staphylococcus aureus USA300 representative. J Bacteriol 194:2924–2938. 10.1128/JB.06708-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

