Supplementation with the Prebiotic High-Esterified Pectin Improves Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Risk Biomarker Profile, Counteracting Metabolic Malprogramming
- PMID: 36214580
- PMCID: PMC9585587
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03143
Supplementation with the Prebiotic High-Esterified Pectin Improves Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Risk Biomarker Profile, Counteracting Metabolic Malprogramming
Abstract
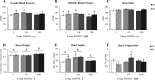
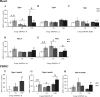
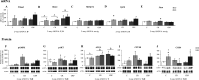
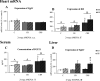
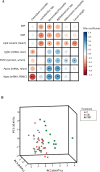
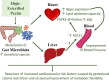
Supplementation with the prebiotic pectin is associated with beneficial health effects. We aimed to characterize the cardioprotective actions of chronic high-esterified pectin (HEP) supplementation (10%) in a model of metabolic malprogramming in rats, prone to obesity and associated disorders: the progeny of mild calorie-restricted dams during the first half of pregnancy. Results show that pectin supplementation reverses metabolic malprogramming associated with gestational undernutrition. In this sense, HEP supplementation improved blood pressure, reduced heart lipid content, and regulated cardiac gene expression of atrial natriuretic peptide and lipid metabolism-related genes. Moreover, it caused an elevation in circulating levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 and a higher expression of its co-receptor β-klotho in the heart. Most effects are correlated with the gut levels of beneficial bacteria promoted by HEP. Therefore, chronic HEP supplementation shows cardioprotective actions, and hence, it is worth considering as a strategy to prevent programmed cardiometabolic alterations.
Keywords: cardiovascular health; high-esterified pectin; microbiota; perinatal malprogramming; prebiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-Esterified Pectin Reverses Metabolic Malprogramming, Improving Sensitivity to Adipostatic/Adipokine Hormones.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Apr 3;67(13):3633-3642. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00296. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30855142
-
Regulation of thermogenic capacity in brown and white adipocytes by the prebiotic high-esterified pectin and its postbiotic acetate.Int J Obes (Lond). 2020 Mar;44(3):715-726. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0445-6. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Int J Obes (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31467421
-
Hypertension Programmed by Perinatal High-Fat Diet: Effect of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy.Nutrients. 2019 Dec 2;11(12):2908. doi: 10.3390/nu11122908. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31810197 Free PMC article.
-
Pectin in diet: Interactions with the human microbiome, role in gut homeostasis, and nutrient-drug interactions.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Mar 1;255:117388. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117388. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33436217 Review.
-
Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits.Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104 Suppl 2:S1-63. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510003363. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20920376 Review.
Cited by
-
The Association between Dietary Fiber Intake and Serum Klotho Levels in Americans: A Cross-Sectional Study from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 14;15(14):3147. doi: 10.3390/nu15143147. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37513564 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Pectin from Lemon Peels.Molecules. 2024 Aug 16;29(16):3878. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163878. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs); https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed 2021-06-30).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

