Asian-Pacific consensus on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in gastrointestinal disorders: An initiative of the Indian Neurogastroenterology and Motility Association
- PMID: 36214973
- PMCID: PMC9549446
- DOI: 10.1007/s12664-022-01292-x
Asian-Pacific consensus on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in gastrointestinal disorders: An initiative of the Indian Neurogastroenterology and Motility Association
Abstract
In the clinical setting, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a frequent, but under-diagnosed entity. SIBO is linked to various gastrointestinal (GI) and non-GI disorders with potentially significant morbidity. The optimal management of SIBO is undefined while there is a lack of published consensus guidelines. Against this background, under the auspices of the Indian Neurogastroenterology and Motility Association (INMA), formerly known as the Indian Motility and Functional Diseases Association (IMFDA), experts from the Asian-Pacific region with extensive research and clinical experience in the field of gut dysbiosis including SIBO developed this evidence-based practice guideline for the management of SIBO utilizing a modified Delphi process based upon 37 consensus statements, involving an electronic voting process as well as face-to-face meetings and review of relevant supporting literature. These statements include 6 statements on definition and epidemiology; 11 on etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology; 5 on clinical manifestations, differential diagnosis, and predictors; and 15 on investigations and treatment. When the proportion of those who voted either to accept completely or with minor reservations was 80% or higher, the statement was regarded as accepted. The members of the consensus team consider that this guideline would be valuable to inform clinical practice, teaching, and research on SIBO in the Asian-Pacific region as well as in other countries.
Keywords: Breath methane; Disorders of gut-brain interaction; Dysbiosis; FODMAP; Gut microbiota; Hydrogen breath test; Irritable bowel syndrome; Rifaximin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
UCG has patent applications for upper gut aspirate culture, FODMAP fermentation chamber, and BreathCalc. KAG is an advisory board member to Adare. GH report to be on the advisory boards of Australian Biotherapeutics, Glutagen, Bayer and received research support from Bayer, Abbott, Pfizer, Janssen, Takeda, Allergan. He serves on the Boards of the West Moreton Hospital and Health Service, Queensland, UQ Healthcare, Brisbane, and the Gastro-Liga, Germany. He has a patent for the Brisbane aseptic biopsy device and serves as Editor of the Gastro-Liga Newsletter. None of the other authors have any conflict of interest to declare in relation to this paper.
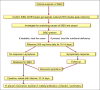
Figures

References
-
- Quigley EMM, Murray JA, Pimentel M. AGA clinical practice update on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Expert review. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1526–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

