Extrahepatic Portal Vein Thrombosis in Childhood: Risk Factors, Clinical Manifestations, and Management
- PMID: 36215953
- PMCID: PMC9841761
- DOI: 10.1159/000527247
Extrahepatic Portal Vein Thrombosis in Childhood: Risk Factors, Clinical Manifestations, and Management
Abstract
Objective: Extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis (EHPVT) is a common cause of portal hypertension in children. The aim of the present study was to identify the clinical manifestations and the risk factors for development of EHPVT in pediatric patients.
Subjects and methods: This was a single-center retrospective cohort study. A total of 12 children (6 boys and 6 girls) took part in the study. We noted the clinical presentations and the predisposing risk factors for development of EHPVT in all patients. In addition, as all of them had undergone an esophagogastroduodenoscopy for detection and grading of esophageal varices as part of the treatment algorithm, we analyzed the endoscopic findings and the therapeutic approach.
Results: The median age of subjects at diagnosis was 3.5 years (range: 1-17 years). The most frequent initial clinical manifestation was upper gastrointestinal bleeding (6 cases, 50.0%) followed by splenomegaly (3 cases, 25.0%). The most frequent systemic risk factor for EHPVT was presence of inherited prothrombotic disorder (10 cases, 83.3%), and the most common local risk factor for EHPVT was umbilical vein catheterization (5 cases, 41.7%). Esophageal varices were revealed in all the study participants, and in the most cases, they were grade ≥2. Propranolol was used as primary or secondary prophylaxis in 7 children (58.3%), and in 5 children (41.7%), a shunt was performed (Meso-Rex bypass in 3 children and splenorenal shunt in 2 children).
Conclusion: Patients with known systemic or local risk factors for EHPVT are indicated for proactive ultrasound screening for early diagnosis and timely management.
Keywords: Extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis; Manifestations; Risk factors.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
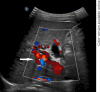
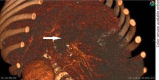
References
-
- Schettino GCM, Fagundes ED, Roquete MLV, Ferreira AR, Penna FJ. Portal vein thrombosis in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2006 May-Jun;82((3)):171–178. - PubMed
-
- Ferri PM, Ferreira AR, Fagundes EDT, Liu SM, Roquete MLV, Penna FJ. Portal vein thrombosis in children and adolescents 20 years experience of a pediatric hepatology reference center. Arq Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan-Mar;49((1)):69–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

