Cut-off values of serum interleukin-6 for culture-confirmed sepsis in neonates
- PMID: 36216867
- PMCID: PMC10313515
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-022-02329-9
Cut-off values of serum interleukin-6 for culture-confirmed sepsis in neonates
Abstract
Introduction: Neonatal sepsis accounts for 0.97% of all disability-adjusted life years worldwide. Interleukin-6 has been used in sepsis diagnosis, but cut-off values are missing.
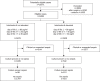
Methods: Neonates admitted to the neonatal wards with measurements of serum interleukin-6 born between September 2015 and September 2019 were retrospectively analysed. Mean serum interleukin-6 values of patients who never had increased laboratory parameters of infection nor died during their stay and mean interleukin-6 values on the day of blood sampling for a later positive culture in patients with culture-confirmed sepsis were analysed for each time period.
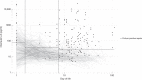
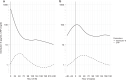
Results: In all, 8.488 values in 1.695 neonates, including 752 very-preterm-infants and 701 very-low-birthweight infants, were analysed. The AUC for interleukin-6 was 0.84-0.91 in all neonates, 0.88-0.89 in very-preterm and 0.89-0.91 in very-low-birthweight infants. Using interleukin-6 cut-off values of 80 pg/ml on day of life 1, 40 pg/ml on day of life 2-7 and 30 pg/ml after day of life 7, a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 81% for culture-confirmed sepsis were achieved. In very-preterm infants, the corresponding values were 74% for sensitivity and 83% for specificity and in very-low-birthweight infants 74% and 86%, respectively.
Conclusion: Serum interleukin-6 has high accuracy for the detection of neonatal sepsis.
Impact: Serum interleukin-6 can be used with high accuracy to detect sepsis in neonates with the cut-off values of 80 pg/ml on day of life 1, 40 pg/ml on day of life 2-7 and 30 pg/ml after day of life 7. Serum interleukin-6 can be used with high accuracy to detect sepsis in neonates and very-preterm as well as very-low-birthweight infants. Interleukin-6 values display distinct cut-off values depending on the chronological age of the infant. Our article provides the first cut-off values for interleukin-6 in the first days of life in neonates.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 in preterm premature rupture of membranes as an indicator of neonatal outcome.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005 Jul;84(7):632-8. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-6349.2005.00747.x. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005. PMID: 15954871
-
Diagnosis of late onset neonatal sepsis with cytokines, adhesion molecule, and C-reactive protein in preterm very low birthweight infants.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 Nov;77(3):F221-7. doi: 10.1136/fn.77.3.f221. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997. PMID: 9462194 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The cut-off levels of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein and the kinetics of mean platelet volume in preterm neonates with sepsis.BMC Pediatr. 2018 Aug 1;18(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-1236-2. BMC Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30068303 Free PMC article.
-
The Sensitivity and Specificity of Procalcitonin in Diagnosing Bacterial Sepsis in Neonates.Hosp Pediatr. 2024 Mar 1;14(3):199-208. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2023-007318. Hosp Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38415310 Review.
-
Management of Neonates Born at ≤34 6/7 Weeks' Gestation With Suspected or Proven Early-Onset Bacterial Sepsis.Pediatrics. 2018 Dec;142(6):e20182896. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2896. Pediatrics. 2018. PMID: 30455344 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential role of heparin-binding protein in neonatal sepsis: research progress.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 13;14:1422872. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1422872. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39193501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of interleukin-6 to identify serious bacterial infections in febrile infants aged ≤60 days.Acta Paediatr. 2025 Jan;114(1):173-179. doi: 10.1111/apa.17422. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Acta Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 39287096 Free PMC article.
-
Management of neonates at risk of early onset sepsis: a probability-based approach and recent literature appraisal : Update of the Swiss national guideline of the Swiss Society of Neonatology and the Pediatric Infectious Disease Group Switzerland.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Dec;183(12):5517-5529. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05811-0. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39417838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Point-of-Care Testing of C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, and Procalcitonin in Neonates with Clinically Suspected Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study.Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(3):291-298. doi: 10.1159/000536678. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38320541 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Biomarkers in Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants: A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 9;13(3):670. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030670. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD Compare | IHME Viz Hub (accessed 27 February 2021); http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

