Irrelevant angry faces impair response inhibition, and the go and stop processes share attentional resources
- PMID: 36216957
- PMCID: PMC9550771
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19116-5
Irrelevant angry faces impair response inhibition, and the go and stop processes share attentional resources
Abstract
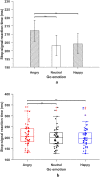
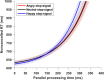
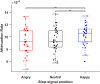
Response inhibition is a crucial component of executive control, which refers to our ability to suppress responses that are no longer needed or inappropriate. The stop-signal task is a standard tool to assess inhibitory control over actions. Here, we use irrelevant facial expressions (happy, angry, or neutral) as both go and stop-signal to examine competition for shared attentional resources between (a) emotion and inhibition process and (b) go and stop processes. Participants were required to respond to go signals (gender discrimination task: male or female). Occasionally, a stop-signal (face with irrelevant angry, happy, or neutral facial expression) was presented, and participants were required to withhold their motor response. We found that emotion processing (especially angry faces) captures attention away from the task, and the emotionality of the stop signal matters only when the go signal is non-emotional. When the go signal was non-emotional, we found that stop-signal with irrelevant angry facial expressions impaired inhibitory control compared to stop-signal with irrelevant happy and neutral facial expressions. These results indicate that the processing of emotion and inhibition process exploit a shared pool of attentional resources. These results favor an interactive capacity-sharing account of the go and stop processes in models of response inhibition.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Only irrelevant angry, but not happy, expressions facilitate the response inhibition.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2021 Jan;83(1):114-121. doi: 10.3758/s13414-020-02186-w. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2021. PMID: 33146816
-
Electrophysiological evidence for attentional capture by irrelevant angry facial expressions.Biol Psychol. 2016 Oct;120:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Biol Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27568328
-
Angry but not neutral faces facilitate response inhibition in schizophrenia patients.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Oct;267(7):621-627. doi: 10.1007/s00406-016-0748-8. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27866272
-
Current status of the anger superiority hypothesis: A meta-analytic review of N2pc studies.Psychophysiology. 2021 Jan;58(1):e13700. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13700. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Psychophysiology. 2021. PMID: 33040366 Review.
-
The neuropsychopharmacology of action inhibition: cross-species translation of the stop-signal and go/no-go tasks.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Aug;199(3):439-56. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1127-6. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18542931 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of aging and valence on emotional response inhibition: conclusions from a novel stop-signal task.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1568492. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1568492. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40276668 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory control towards angry stimuli in patients with binge eating disorder: a pilot study.J Eat Disord. 2023 Jul 31;11(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s40337-023-00848-2. J Eat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37525245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yiend J. The effects of emotion on attention: A review of attentional processing of emotional information. Cogn. Emot. 2010;24:3–47. doi: 10.1080/02699930903205698. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

