The aldolase inhibitor aldometanib mimics glucose starvation to activate lysosomal AMPK
- PMID: 36217034
- PMCID: PMC9584815
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00640-7
The aldolase inhibitor aldometanib mimics glucose starvation to activate lysosomal AMPK
Abstract
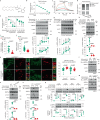
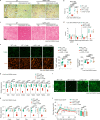
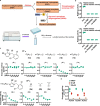
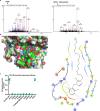
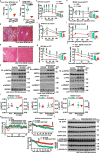
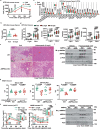
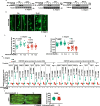
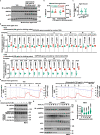
The activity of 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is inversely correlated with the cellular availability of glucose. When glucose levels are low, the glycolytic enzyme aldolase is not bound to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) and, instead, signals to activate lysosomal AMPK. Here, we show that blocking FBP binding to aldolase with the small molecule aldometanib selectively activates the lysosomal pool of AMPK and has beneficial metabolic effects in rodents. We identify aldometanib in a screen for aldolase inhibitors and show that it prevents FBP from binding to v-ATPase-associated aldolase and activates lysosomal AMPK, thereby mimicking a cellular state of glucose starvation. In male mice, aldometanib elicits an insulin-independent glucose-lowering effect, without causing hypoglycaemia. Aldometanib also alleviates fatty liver and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in obese male rodents. Moreover, aldometanib extends lifespan and healthspan in both Caenorhabditis elegans and mice. Taken together, aldometanib mimics and adopts the lysosomal AMPK activation pathway associated with glucose starvation to exert physiological roles, and might have potential as a therapeutic for metabolic disorders in humans.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The compounds described in this paper have been filed for a patent application (WO 2018184561). Authors X.D., C.-S.Z. and S.-C.L. are listed as inventors on the patent (WO 2018184561) on the therapeutic use of aldometanib and other aldometanib derivatives. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Carling D, Clarke PR, Zammit VA, Hardie DG. Purification and characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Copurification of acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989;186:129–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15186.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

