Elevated vascular transformation blood biomarkers in Long-COVID indicate angiogenesis as a key pathophysiological mechanism
- PMID: 36217108
- PMCID: PMC9549814
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-022-00548-8
Elevated vascular transformation blood biomarkers in Long-COVID indicate angiogenesis as a key pathophysiological mechanism
Abstract
Background: Long-COVID is characterized by prolonged, diffuse symptoms months after acute COVID-19. Accurate diagnosis and targeted therapies for Long-COVID are lacking. We investigated vascular transformation biomarkers in Long-COVID patients.
Methods: A case-control study utilizing Long-COVID patients, one to six months (median 98.5 days) post-infection, with multiplex immunoassay measurement of sixteen blood biomarkers of vascular transformation, including ANG-1, P-SEL, MMP-1, VE-Cad, Syn-1, Endoglin, PECAM-1, VEGF-A, ICAM-1, VLA-4, E-SEL, thrombomodulin, VEGF-R2, VEGF-R3, VCAM-1 and VEGF-D.
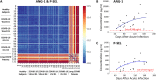
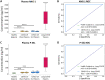
Results: Fourteen vasculature transformation blood biomarkers were significantly elevated in Long-COVID outpatients, versus acutely ill COVID-19 inpatients and healthy controls subjects (P < 0.05). A unique two biomarker profile consisting of ANG-1/P-SEL was developed with machine learning, providing a classification accuracy for Long-COVID status of 96%. Individually, ANG-1 and P-SEL had excellent sensitivity and specificity for Long-COVID status (AUC = 1.00, P < 0.0001; validated in a secondary cohort). Specific to Long-COVID, ANG-1 levels were associated with female sex and a lack of disease interventions at follow-up (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Long-COVID patients suffer prolonged, diffuse symptoms and poorer health. Vascular transformation blood biomarkers were significantly elevated in Long-COVID, with angiogenesis markers (ANG-1/P-SEL) providing classification accuracy of 96%. Vascular transformation blood biomarkers hold potential for diagnostics, and modulators of angiogenesis may have therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Biomarkers; Long-COVID; Machine learning; Vascular transformation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
V.D., M.M. and B.W. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. who manufacture and distribute multiplex immunoassays as research use only reagents. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bradley AP. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recogn. 1997;30:1145–1159. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(96)00142-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

