Circular RNA circRASSF5 Functions as an Anti-Oncogenic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Acting as a Competitive Endogenous RNA Through Sponging miR-331-3p
- PMID: 36217445
- PMCID: PMC9547604
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S376063
Circular RNA circRASSF5 Functions as an Anti-Oncogenic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Acting as a Competitive Endogenous RNA Through Sponging miR-331-3p
Abstract
Objective: Recently, emerging studies have validated that circular RNAs participate in multiple biological progresses in various human malignant tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, until now, the elucidated mechanism of circular RNAs is only the tip of the iceberg. In this study, we firstly identify a novel circular RNA circRASSF5 (the only circular RNA derived from the RASSF5 gene), and attempt to investigate its biological function and underlying mechanism in HCC.
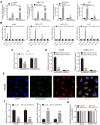
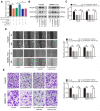
Methods: qRT-PCR, Western blotting and IHC were applied to detect the expression of related genes. CCK-8 assay, EdU staining, wound healing and transwell assays were used to investigate HCC proliferation, migration and invasion abilities. Animal model studies were included to investigate the function of circRASSF5 in HCC tumorigenesis and metastasis. RNA pull-down assay, luciferase reporter assay and FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) assay were performed to explore the potential biological mechanism underlying circRASSF5 function in HCC.
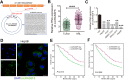
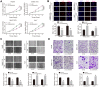
Results: CircRASSF5 is obviously downregulated in both HCC tissues and cell lines. Low level of circRASSF5 is negatively associated with larger tumor size, severe vascular invasion, more portal vein tumor embolus and unfavorable prognosis. Loss-of-function assay reveals that circRASSF5 remarkably impedes the growth and metastasis of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, circRASSF5 directly interacts with miR-331-3p as a sponge, and then enhances the expression of PH domain and leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase (PHLPP), thus restraining the progression of HCC cells.
Conclusion: Altogether, we validate that circRASSF5 is a tumor suppressor in HCC, which competitively sponges with miR-331-3p and then enhances the tumor inhibitory effect of PHLPP, indicating the potential application value of circRASSF5 for HCC diagnosis and clinical treatment.
Keywords: HCC; PHLPP; circRASSF5; miR-331-3p.
© 2022 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circular RNA circZNF566 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-4738-3p and regulating TDO2 expression.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 12;11(6):452. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2616-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32532962 Free PMC article.
-
CircCCNB1 silencing acting as a miR-106b-5p sponge inhibited GPM6A expression to promote HCC progression by enhancing DYNC1I1 expression and activating the AKT/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):637-651. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66915. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002514 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA CircEPB41L2 Functions as Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Sponging miR-590-5p.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Apr 1;13:2969-2981. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S291682. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33833580 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of hsa_circ_0101145 reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the miR-548c-3p/LAMC2 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 18;12(12):11623-11635. doi: 10.18632/aging.103324. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32554866 Free PMC article.
-
CircWHSC1 serves as an oncogene to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Jun;51(6):e13487. doi: 10.1111/eci.13487. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33410156
Cited by
-
Differentially expressed non-coding RNAs and their regulatory networks in liver cancer.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 19;9(9):e19223. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19223. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37662778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of the miRNA/Pyroptosis-Related Molecular Regulatory Axis in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Evidence From Transcriptome Data Combined With Multiple Machine Learning Approaches Followed by Experiment Validation.J Immunol Res. 2024 Oct 30;2024:1429510. doi: 10.1155/2024/1429510. eCollection 2024. J Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39512836 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Sep 13;18(1):20230795. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0795. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37724126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asafo-Agyei KO, Samant H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2021. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

