Synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-thymol derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents
- PMID: 36217474
- PMCID: PMC9547220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10836
Synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-thymol derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents
Abstract
Background: Thymol as a natural biological template can be modified chemically since the hydroxyl group makes it a candidate for structural modification. Thus, this study incorporated the triazole moiety on thymol and the chlorination of thymol moiety to help improve its biological potency.
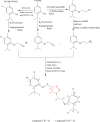
Materials and methods: A series of ten 1,2,3-triazole-thymol derivatives 1-10 were synthesized from thymol, by a click reaction between O-propargyl terminal alkyne of thymol and its chlorothymol with benzyl azide and substituted benzyl azides. Their structures were confirmed by spectroscopic methods (1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR, GC-MS-EI/CI and LC-ESI-QTOF-MS). The Well diffusion method using Müeller-Hinton agar plates was used to demonstrate the antimicrobial activities of the synthesized triazole-thymol derivatives on selected bacterial strains; Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923, Methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 29853, E. coli ESBL, K l ebsiella pneumoniae NCTC 13438 and Meropenem Resistant E. coli.
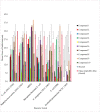
Results: All the synthesized triazole-thymol derivatives showed significant but variable antibacterial activity against the seven medically important bacterial strains tested. The compound 4-((4-chloro-2-isopropyl-5-methylphenoxy)methyl)-1-(2-nitrobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3triazole (9) demonstrated a higher antibacterial activity with a mean zone of inhibition (38.7 mm) compared with ampicillin as the positive control which gave a zone size of 30.0 mm. In addition, the compound showed a three-fold potency than the parent compound, thymol (11.0 mm) against MRSA at a concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Conclusion: These results provide additional evidence of the exploitation of natural products like thymol as leads for drug development against medically important bacterial pathogens.
Keywords: Ampicillin; Antibacterial activity; Essential oil; Monoterpenoid; Thymol; Triazole.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kachur K., Suntres Z. The antibacterial properties of phenolic isomers, carvacrol and thymol. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020;60:3042–3053. - PubMed
-
- Ghomi J.S., Meshkatalsadat M.H., Shamat S., Hasheminejad M., Hassani A. Chemical characterization of bioactive volatile molecules of four thymus species using nanoscale injection method. Digest. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2009;4:835.
-
- Pathak A.K., Nainwal N., Goyal B.M., Singh R., Mishra V., Nayak S., Gupta V. Pharmacological activity of Trachyspermum ammi: a review. J. Pharm. Res. 2010;3:895–899.
-
- Vazquez B.I., Fente C., Franco C.M., Vazquez M.J., Cepeda A. Inhibitory effects of eugenol and thymol on Penicillium citrinum strains in culture media and cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001;67:157–163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

