Meta-Analysis of the Application Effect of Different Modalities of Thermal Ablation and Surgical Treatment in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
- PMID: 36217504
- PMCID: PMC9547687
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9714140
Meta-Analysis of the Application Effect of Different Modalities of Thermal Ablation and Surgical Treatment in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Meta-Analysis of the Application Effect of Different Modalities of Thermal Ablation and Surgical Treatment in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9819468. doi: 10.1155/2023/9819468. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 38077933 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) refers to papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with a maximum diameter of 10 mm. Thermal ablation, including radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and laser ablation (LA), has been applied in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules and captured extensive attention. At present, the application of thermal ablation in PTMC has been extensively reported, but outcomes such as volume reduction rate (VRR), complete remission rate (CRR), and adverse reaction rate (ARR) vary considerably. Therefore, this meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of different treatment methods of PTMC.
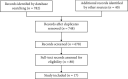
Methods: We did a systematic review and network meta-analysis. We searched PubMed, EMBase, and Cochrane-Library from the date of inception to January 10, 2022, to retrieve the VRR, CRR, and ARR of MWA, RFA, LA and surgical treatment of PTMC, and a meta-analysis was performed using the R meta-package. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated, and sensitivity analyses, cumulative meta-analyses, and publication bias were also performed. Relevant literature was retrieved with keywords; the eligible cohort studies were screened based on the established inclusion and exclusion criteria.
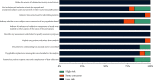
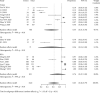
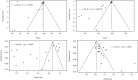
Results: A total of 1515 patients were included in the 12-month follow-up. The overall VRR was 86.25% (95% CI: 77.89, 94.60), and the VRR was RFA > WMA > LA, but the differences were not significant. A total of 1483 patients were included in the last follow-up. The overall VRR was 99.41% (95% CI: 99.11, 99.72), and the VRR was RFA > WMA > LA, but the differences were not significant. A total of 1622 patients showed complete remission at the last follow-up, and the overall CRR was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.46, 0.79). The CRR was RFA > LA > WMA, but the differences were not significant. A total of 1883 patients had adverse reactions at the last follow-up, and the overall ARR was 0.06 (95% CI: 0.03, 0.08). The ARR at the last follow-up was RFA = Surg < LA < WMA. The ARR of the RFA and Surg subgroups was significantly lower than that of the WMA subgroup.
Conclusions: Similar good efficacy and safety profiles were observed in WMA, RFA, LA, and surgical treatment in PTMC, among which RFA showed the best volume reduction, complete remission rate, and adverse reaction reduction. However, there is a slight bias in the limited literature included in this study, and we did not conduct or refer to mechanistic studies to confirm its specific mechanism of action. Clinicians are advised to use their discretion in the choice of treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Tao Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy of different thermal ablation and conventional surgery for the treatment of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Systematic review including traditional pooling and Bayesian network meta-analysis.Am J Otolaryngol. 2024 Nov-Dec;45(6):104479. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2024.104479. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Am J Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39111026
-
Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency, microwave and laser ablation for the treatment of T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma on a large scale: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Hyperthermia. 2023 Dec;40(1):2244713. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2023.2244713. Int J Hyperthermia. 2023. PMID: 37604507
-
A Prospective Clinical Trial of Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Unifocal Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma Favoring Active Surveillance Over Surgery.Thyroid. 2024 Sep;34(9):1126-1136. doi: 10.1089/thy.2024.0098. Thyroid. 2024. PMID: 39212950 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimally Invasive Treatments of Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Network Meta-Analysis of Short-Term Outcomes.Thyroid. 2023 Aug;33(8):950-964. doi: 10.1089/thy.2022.0671. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Thyroid. 2023. PMID: 37166390
-
Ultrasound‑guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation for Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta‑analysis of Clinical Efficacy and Safety.Acad Radiol. 2025 May;32(5):2533-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.12.064. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39800601
Cited by
-
Retracted: Meta-Analysis of the Application Effect of Different Modalities of Thermal Ablation and Surgical Treatment in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9819468. doi: 10.1155/2023/9819468. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 38077933 Free PMC article.
-
Transitioning from Traditional Academic Decision Making to Patient-Centric Healthcare Choices: The Example of Thyroid Thermal Ablation Techniques for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas.Curr Oncol. 2023 Oct 31;30(11):9670-9675. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30110701. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37999121 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

