Efficacy of Immunomodulatory Drugs in Combination With Dexamethasone in Proliferative Glomerulonephritis With Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposits
- PMID: 36217516
- PMCID: PMC9546741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.07.009
Efficacy of Immunomodulatory Drugs in Combination With Dexamethasone in Proliferative Glomerulonephritis With Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposits
Abstract
Introduction: Immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) plus dexamethasone are effective for plasma cell dyscrasias, but the treatment efficacy of IMiD in proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits (PGNMID) has been rarely reported.
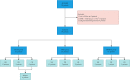
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinicopathologic data of 64 patients with PGNMID (steroid, IMiD, and bortezomib and dexamethasone/Rituximab [BD/RTX] groups) from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2020, at the National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Disease in Nanjing. The prognosis of patients receiving different treatment regimens were compared. Factors potentially affecting renal prognosis and renal response were evaluated.
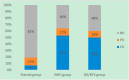
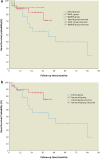
Results: Twenty-eight, 26 and 10 PGNMID patients were divided into IMiD group, steroid group and BD/RTX group respectively. The rate of serum M protein detection was significantly lower in the steroid group than in the other 2 groups. Renal remission (P = 0.001 and P = 0.03, respectively) rates and renal complete remission (CR) (P = 0.001 and P = 0.01, respectively) rates were significantly higher in the IMiD and BD/RTX groups than in the steroid group at the last follow-up. Multivariate logistic analysis identified that hypertension and high serum creatinine (SCr) levels (>1.24 mg/dl) decreased renal remission, whereas low C3 levels, IMiD and BD/RTX treatments were positively associated with renal remission. Multivariate Cox analysis identified IgG3 in renal tissue and high SCr levels as poor renal prognostic indicators. Severe adverse events were more common in the IMiD and BD/RTX groups than in the steroid group (P = 0.072 and P = 0.035, respectively).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that IMiDs plus dexamethasone is effective for achieving renal remission in PGNMID patients.
Keywords: efficacy; immunomodulatory drug; proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits; renal prognosis.
© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful treatment with bortezomib and dexamethasone for proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal IgG deposits in multiple myeloma: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Apr 6;18(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0524-7. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28385149 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits: an entity associated with distinct diseases and comparison between IgG1 and IgG3 subtypes.J Nephrol. 2022 Dec;35(9):2363-2372. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01317-w. Epub 2022 Apr 23. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35460458
-
The Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of Patients with Proliferative Glomerulonephritis with Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposits.Glomerular Dis. 2025 Feb 20;5(1):142-150. doi: 10.1159/000544864. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Glomerular Dis. 2025. PMID: 40134832 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin G deposits complicated by immunoglobulin A nephropathy in the renal allograft.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Jul;21 Suppl 1:48-52. doi: 10.1111/nep.12775. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26971743 Review.
-
Treatment with bortezomib for recurrent proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal IgG deposits in kidney allograft. Case report and review of the literature.J Nephrol. 2022 May;35(4):1289-1293. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01332-x. Epub 2022 May 6. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35522429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Outcomes of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Renal Significance Without Detectable Clones.Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Sep 22;8(12):2765-2777. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.09.022. eCollection 2023 Dec. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 38106576 Free PMC article.
-
Hemato-Renal Profile of Proliferative Glomerulonephritis with Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposits.Indian J Nephrol. 2024 Jul 22;35(3):355-367. doi: 10.25259/ijn_489_23. Indian J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39850252 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferative Glomerulonephritis With Monoclonal Ig Deposits Without Detectable Clones: Navigating Empirical Clone-Directed Therapy.Kidney Int Rep. 2025 Apr 21;10(7):2480-2483. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.04.031. eCollection 2025 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2025. PMID: 40677329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Uncertainty Puzzle of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Renal Significance Without Detectable Clones.Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Oct 18;8(12):2511-2514. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.10.013. eCollection 2023 Dec. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 38106591 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Case report: A case of proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal kappa-light chain deposits treated with daratumumab combination therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 2;11:1462199. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1462199. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39416872 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

