Quality of Chinese government environmental health information disclosure during COVID-19 pandemic: Satisfaction survey on University students
- PMID: 36217540
- PMCID: PMC9546724
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.948172
Quality of Chinese government environmental health information disclosure during COVID-19 pandemic: Satisfaction survey on University students
Abstract
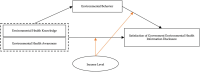
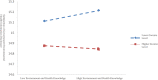
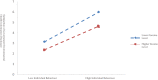
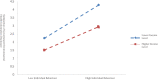
Government played a vital role during the COVID-19 pandemic by disclosing related environmental health information to the public. A satisfaction survey is often used to evaluate the public's satisfaction of the government's information disclosure while reflecting problems in the current disclosure system. As University students generally have better cognitive skills, they efficiently received related information during the pandemic, and therefore 717 questionnaires completed by University students were selected for this study. During the pandemic, the quality of the government's environmental health information disclosure system ranked at 13.89, marginally higher than average. Moreover, the timeliness and content adequacy of the disclosure system ranked at a level slightly above average. By adopting Hayes PROCESS Model 4 and 8, this study found that there is a direct impact of environmental health knowledge and environmental health awareness on satisfaction. Furthermore, University students' environmental health knowledge and awareness enhanced satisfaction through the mediating effect of self-reported environmental behavior. Finally, this study attempted to discover the conditions under which environmental health knowledge and awareness would have a greater direct and indirect influence on satisfaction, that is, the reverse moderating effect of household income level. In addition, this paper offers policy recommendations to enhance quality of government environmental health information disclosure system.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; environmental behavior; environmental health awareness; environmental health knowledge; environmental health knowledge disclosure; quality of government information disclosure.
Copyright © 2022 An, Wang, Hou and Hideki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization [Internet] . WHO: Timeline: WHO's COVID-19 Response. (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact... (accessed August 8, 2022).
-
- Ge S, Li J, Zhang S, Deng H. Data analysis report of 2020 epidemic. In: 2020 Data Creator Conference, Shanghai, Sep 17, 2020; Shanghai: The Paper; (2020). Available online at: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_9182883 (accessed on October 29, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

